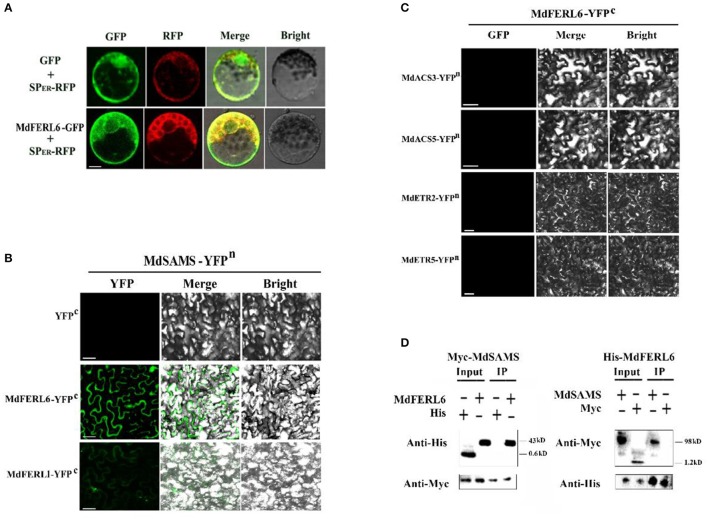
Figure 7.
Subcellular localization of MdFERL6 and its physical interaction with proteins involved in ethylene production and signal transduction. (A) Subcellular localization of MdFERL6. pMDC83-MdFERL6 was transformed into maize (Zea mays) protoplasts, and fluorescence was observed by confocal microscopy. Bars = 10 μm. (B) Bimolecular fluorescence complementation (BiFC) analysis of the physical interaction between MdFERL1 or MdFERL6 and MdSAMS, fused with the C-, C-, and N-terminus, respectively, of yellow fluorescent protein (YFP; designated as YFPc or YFPn, respectively). Different combinations of the fused constructs were co-transformed into tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) cells, and visualized using confocal microscopy. YFP and bright-field were excited at 488 nm and 543 nm, respectively. Bars = 20 μm. (C) BiFC analysis of the physical interaction between MdFERL6 and MdACS3, MdACS5, MdETR2, and MdETR5. MdFERL6 was fused to the C-terminus of YFP, while the other proteins were fused to the N-terminus of YFP. (D) Co-immunoprecipitation (Co-IP) assay of the interaction between MdFERL6 and MdSAMS in apple calli. MdFERL6 was fused with GFP/His using the pMDC83 vector, and MdSAMS was fused with Myc using the pCambia1300 vector. (The molecular weight of Myc-MdSAMS is 43 kD, Myc is 1.2 kD, His-MdFERL6 is 98 kD, and 6 × His is 0.6 kD).