FIG. 1.
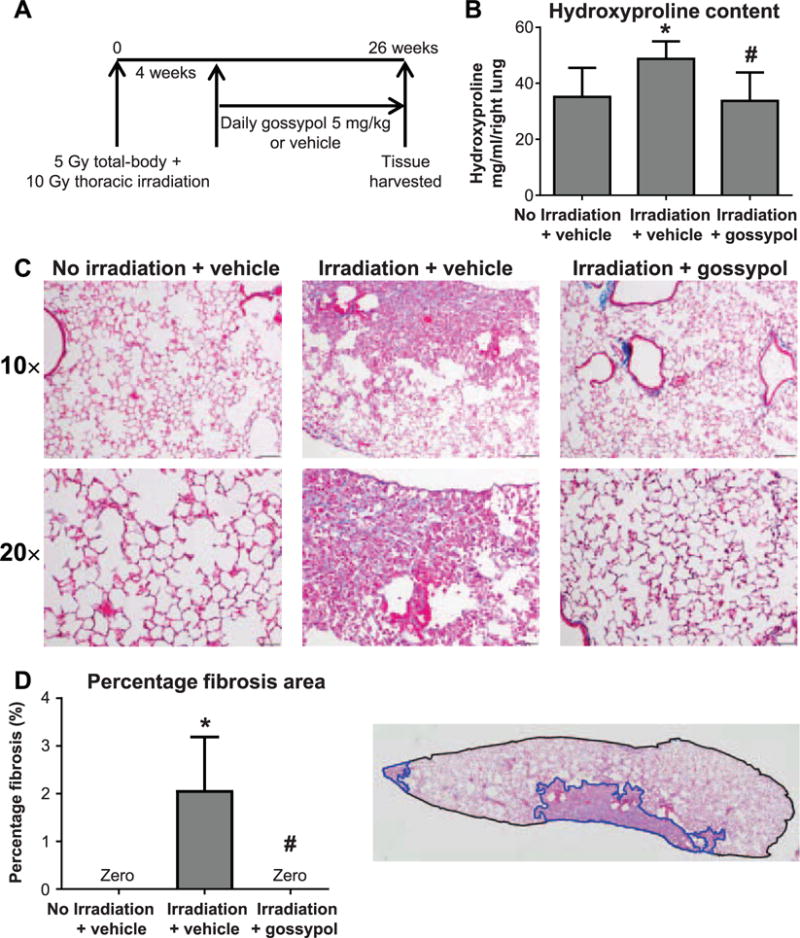
The LDHA inhibitor gossypol inhibits radiation-induced pulmonary fibrosis. Panel A: Mice received 5 Gy total-body irradiation plus 10 Gy thoracic ionizing irradiation from a 137Cs gamma radiation source and were treated with 5 mg/kg/day gossypol or vehicle beginning at week 4 postirradiation until week 26 postirradiation when lung tissue was harvested. Panel B: The right lung was analyzed for collagen content by hydroxyproline assay. Panel C: The left lung was formalin fixed, paraffin embedded and stained for collagen fibers using Gomori Trichrome. One representative mouse is shown from each treatment group. Images were taken at 10× and 20× magnification, and scale bars represent 100 μm. Panel D: Percentage fibrosis area was determined by drawing regions of interest (ROIs) around entire lung sections, and regions of fibrosis. One representative mouse section is shown; total lung section area is outlined in black, fibrotic lesions are outlined in blue. Total and fibrotic area were quantified as described in Materials and Methods. Data are shown as mean ± SEM for 5–6 sections per mouse and n = 7–10 mice per group. *P ≤ 0.05 compared to nonirradiated vehicle-treated controls; #P ≤ 0.05 compared to irradiated vehicle-treated mice (ANOVA).
