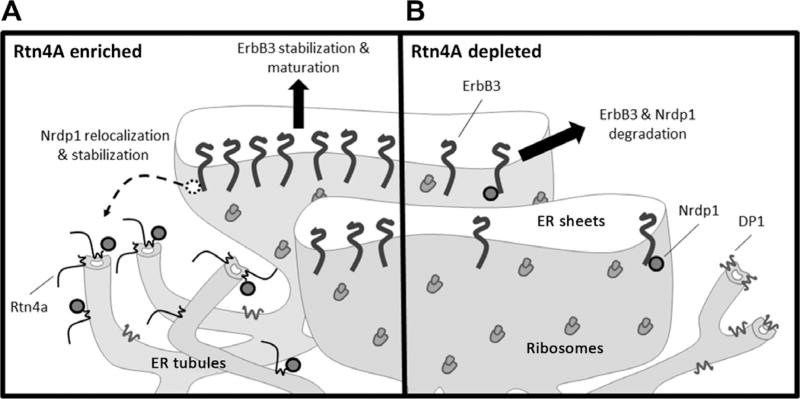
Fig. 7. Rtn4A regulates ErbB3 through sequestration of Nrdp1.
(A) In the presence of Rtn4A, Nrdp1 relocalizes from ER sheets to interact with Rtn4A in ER tubules. Nrdp1 sequestered in ER tubules is unable to mediate the degradation of itself or ErbB3, allowing the receptor to exit ER sheets, mature, and traffic to the plasma membrane where it responds to NRG to promote cell growth and survival. (B) When Rtn4A is depleted, Nrdp1 is free to interact with ErbB3 in ER sheets, leading to the proteasomal degradation of newly synthesized ErbB3, thus decreasing cell growth and survival. The ER tubule structure may be maintained by other structural proteins such as DP1.