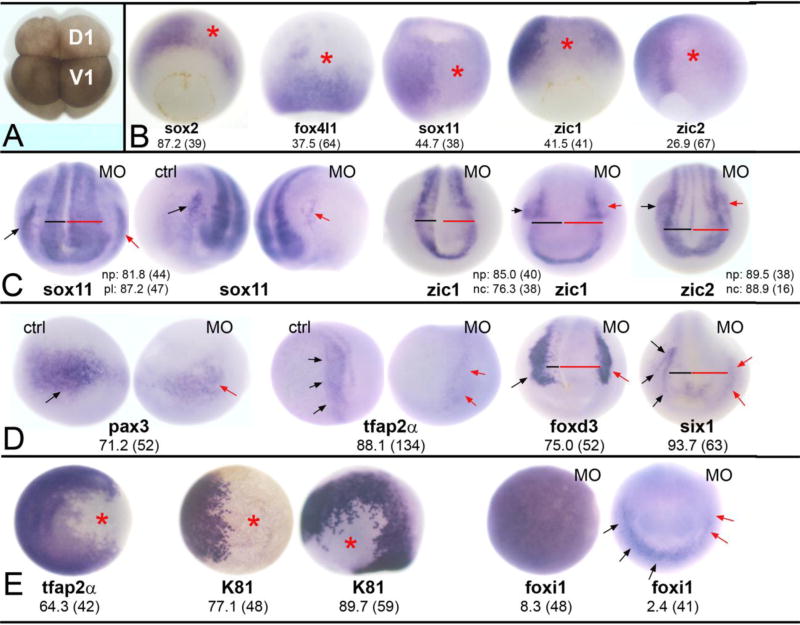
Figure 2. Reduction of Wbp2nl affects ectodermal tissues.
(A) An 8-cell Xenopus laevis embryo. The dorsal-animal blastomere (D1) gives rise to the neural plate and the ventral-animal blastomere (V1) gives rise to the epidermis. Border zone derivatives (neural crest and cranial placodes) descend from the lateral regions of both blastomeres (Moody and Kline, 1990). (B) Knock-down of Wbp2nl causes a decrease in the expression (loss of blue reaction product) of neural ectodermal genes on the MO-injected side (asterisk) of gastrula stage embryos. sox2 is a vegetal view with dorsal to the top; the rest are dorsal views with animal to the top. (C) By neural plate stages, neural gene domains are expanded; compare the width of the neural plate on MO-injected side (red bar) to control side (black bar). (See also D). The PPE domains of sox11 and the neural crest domains of zic1 and zic2 are reduced on MO-injected sides (red arrows) compared to control sides (black arrows). Anterior views with dorsal to the top. (D) At neural plate stages, neural crest markers (pax3, tfap2α, foxd3) and an early PPE marker (six1) are reduced on the MO-injected side (red arrows) compared to control sides (black arrows). Also note wider neural plates (red bars). pax3 and tfap2α are anterior-side views; foxd3 and six1 are anterior views. (E) Two epidermal genes are reduced at the sites of Wbp2nl knock-down (asterisks) at gastrula (tfap2α, K81 right image; both are animal pole views) and neural plate (K81 left image; side view with dorsal to top and anterior to right) stages. In contrast, the animal pole expression of foxi1 in the gastrula (left image) is not altered. Rarely, the PPE expression of foxi1 (right image; anterior view with dorsal to top) is reduced (red arrows) after Wbp2nl knockdown. Frequencies of the phenotypes and sample sizes (n) are given in each panel.