Figure 2. To mount an effective immune response, peptide-MHC-I complexes generated by cross-presentation need to match those generated by the conventional MHC-I presentation pathway.
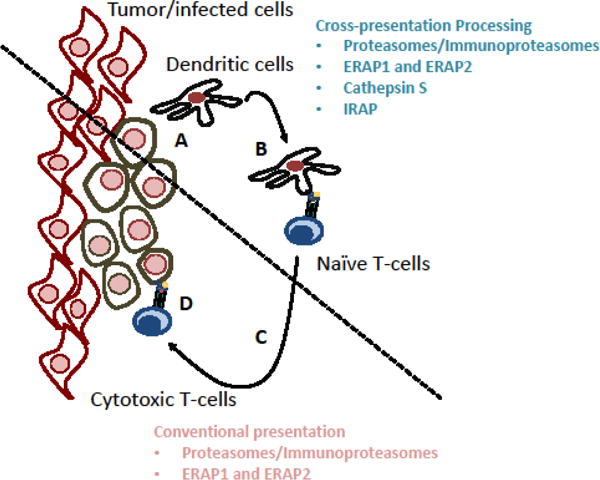
(A) Dendritic cells phagocytose/endocytose antigens from infected tissue. (B) These dendritic cells process and present antigenic peptides, generated by cross-presentation and loaded onto MHC-I, to naïve CD8-positive T-cells, priming them. (C) The primed T-cells migrate to the infected tissue and, (D), recognize peptide-MHC-I presented by infected cells and eliminate them. An effective response requires presentation of the same peptides by DCs (involving cross-presentation) and infected/tumor cells (involving conventional MHC-I antigen presentation). Processing of antigens by the conventional pathway depends on proteasomes and in some cases ER aminopeptidases. Along with proteasomes and ERAPs, cross-presentation can also depend on IRAP and cathepsin S.
