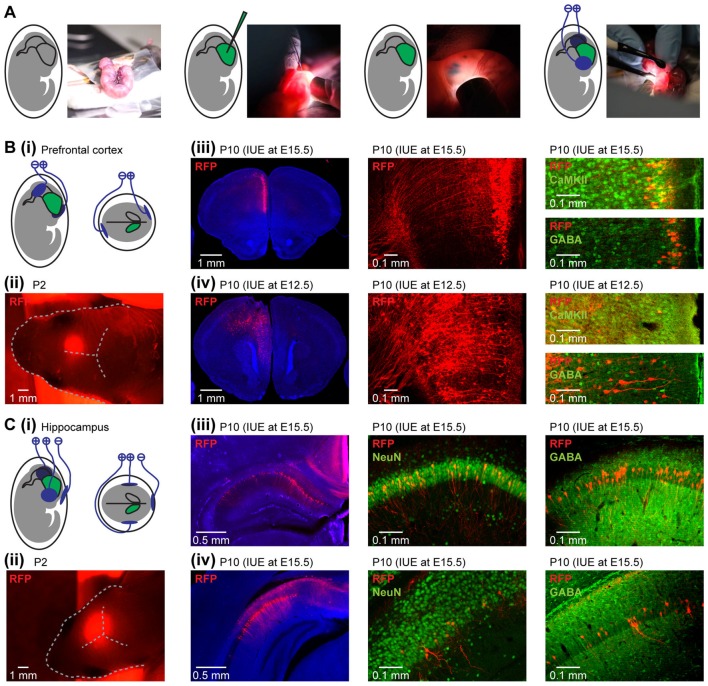
Figure 1.
Area-, layer- and cell-type-specificity of neuronal targeting by in utero electroporation (IUE). (A) Diagrams and photographs illustrating the procedure for IUE. (Bi) Schematic representation of the position of electroporation paddles to yield expression in pyramidal neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex (PFC). (ii) Photograph showing the expression of red fluorescent protein (RFP; red) transfected in the PFC by IUE detectable through skull and skin at P2. (iii) Targeting of pyramidal neurons in layer II/III of the neonatal PFC. Left, RFP expressing cells (red) in 50 μm-thick coronal slices of a P10 mouse at the level of the PFC after IUE at E15.5. Middle, RFP-expressing neurons in prefrontal layer II/III displayed at higher magnification. Right, confocal images of RFP-expressing neurons after staining for Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) or gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). (iv) Targeting of pyramidal neurons in layer V/VI of the neonatal PFC. Same as (iii) for IUE at E12.5. (Ci) Schematic representation of the position of the electroporation paddles to yield expression in pyramidal neurons of hippocampal CA1 area. (ii) Photograph showing the expression of RFP (red) transfected in the hippocampus (HP) by IUE detectable through skull and skin at P2. (iii) Targeting of pyramidal neurons in dorsal hippocampus (HP). Left, RFP expressing cells (red) in 50 μm-thick coronal slices of a P10 mouse at the level of the dorsal HP after IUE at E15.5. Middle, RFP-expressing neurons in dorsal HP displayed at higher magnification after staining for NeuN. Right, confocal images of RFP-expressing neurons after staining for GABA. (iv) Same as (iii) for the intermediate HP.