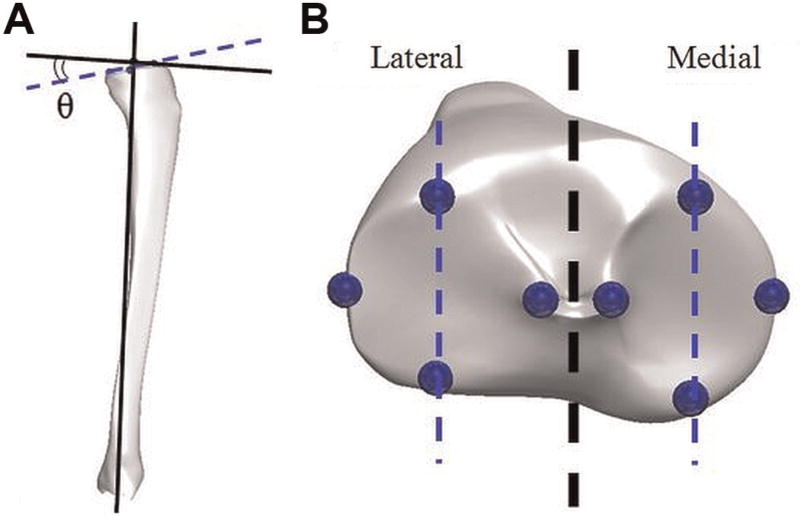
Figure 1.
(A) Depiction of the method used to calculate tibial slope angle, which was the angular difference θ between a line perpendicular to the mechanical axis of the tibia in the sagittal plane and a line passing through the anterior- and posterior-most points of each tibial compartment. The slope shown is positive. (B) Points collected by the coordinate measuring machine for calculation of tibial slope angle. Notice that the anterior- and posterior-most points of the articulating surface fall on the midline of each tibial compartment.