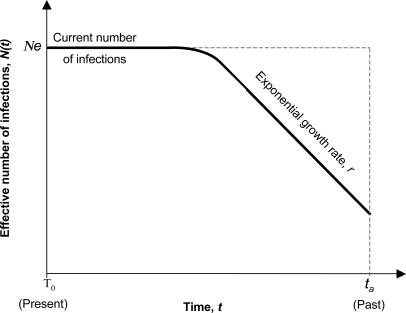
Fig. 3.
Schematic representation of the logistic model of population growth. According to this model, the number of infections population grows exponentially at rate r from time ta (time of the most recent common ancestor of the sampled sequences). The growth rate slows as time moves toward the present, such that Ne represents the effective number of infections at the present. Ne can be thought of as the number of infections contributing to new infections rather than the total number of prevalent infections within the cluster.