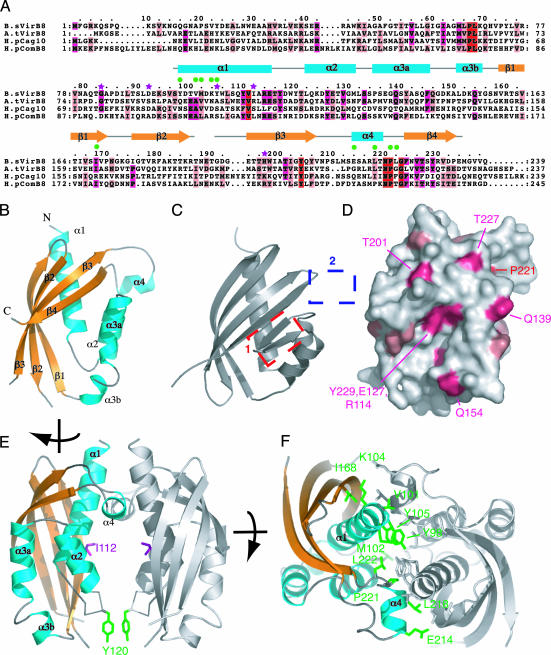
Fig. 1.
Crystal structure of B. suis pVirB8. (A) Sequence alignment of VirB8 proteins and secondary structure assignment. Amino acids of four representative homologs were aligned, from B. suis (B.sVirB8), A. tumefaciens (A.tVirB8, 21% identical to B.sVirB8), H. pylori Cag [H.pCag10 (HP0530, 14% identity], and ComB [H.pComB8 (HP0030), 18% identity] systems (38). Strictly conserved, strongly conserved, and conserved residues are marked in red, magenta, and light pink, respectively. The modeled region (residues 97–188 and 191–234) is shown as a gray line above the sequence for nonregular structure or as cyan boxes and yellow arrows for α-helices and β-strands, respectively. Green dots mark residues involved in VirB8 self association. Purple stars indicate residues mutated in previous functional studies. (B) Overall fold of pVirB8. Secondary structure representation and labels are as in A. (C) Structure of NTF2, most similar fold to pVirB8. Boxes mark the two major points of difference between the NTF2 and pVirB8 fold, the addition of α4 (blue box), and the loss of two β strands (red box). (D) Surface representation of VirB8 coloring side chains by degree of conservation, as shown in A. Orientation is as in B. (E) pVirB8 dimer. Both monomers are shown in ribbon representation with the monomer on the left shown as in B but turned ≈90° clockwise. The other monomer is in gray. Ile-112 and Tyr-120 are shown in stick representation and colored in magenta and green, respectively. (F) Top-down view of pVirB8 dimer showing side chains involved in interface as marked in A. For clarity, one pVirB8 chain is colored gray, and the other is colored as in B. Residues at the interface are in stick representation, color-coded in green, and labeled. The figure was produced by using pymol, http://pymol.sourceforge.net.