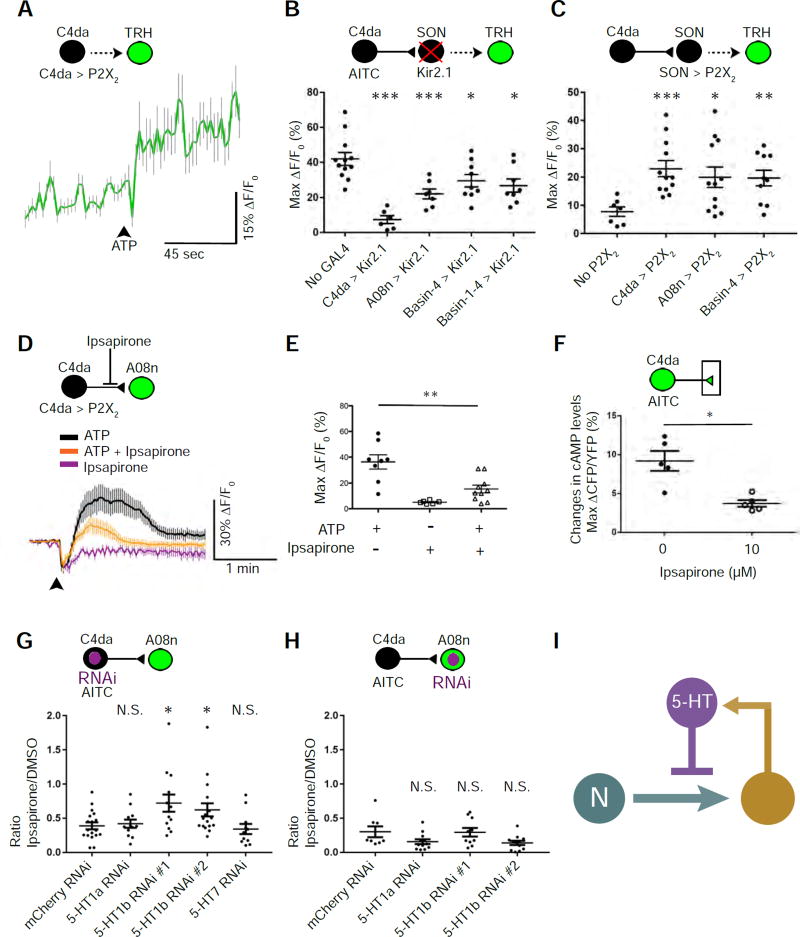
Figure 5. Feedback inhibition of nociceptor-to-SON transmission through serotoninergic neurons.
(A) Stimulating C4da nociceptors activates serotonergic neurons. The trace shows the averages of GCaMP6f intensities in TRH neurons caused by stimulating C4da neurons via ATP/P2X2. The black arrowhead indicates the start of ATP/P2X2-mediated stimulation. n = 33.
(B) Silencing SONs suppresses nociceptor-induced activation of serotonergic neurons. C4da, A08n, Basin-4, and Basin-1–4 were inhibited by expressing Kir2.1. AITC was used to stimulate C4da neurons. n = 12, 6, 7, 9, and 8 larvae in control, C4da, A08n, Basin-4, and Basin-1–4 groups, respectively.
(C) Stimulation of SONs activates serotonergic neurons. ATP was used to activate neurons expressing P2X2. Larvae in “No P2X2” group had no P2X2 expression due to the lack of a GAL4 driver and a P2X2 transgene. n = 7, 12, 12, and 10 larvae in control, C4da, A08n, and Basin-4 groups, respectively.
(D & E) Ipsapirone (100 µM) inhibits C4da-to-A08n synaptic transmission. ATP/P2X2 was used to activate C4da neurons. (D) Traces show the averages of responses. (E) Quantification and statistical analysis (n = 8, 6, 10 neurons, 5 larvae per group).
(F) Ipsapirone (10 µM) diminishes AITC-elicited increase in cAMP levels in C4da axon terminals. Imaging-based cAMP sensor, Epac1-camps, was expressed specifically in nociceptors, and their presynaptic terminals were imaged for Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET). AITC was used to activate nociceptors. Levels of cAMP were quantified as changes in the inverse FRET ratio, which is CFP intensity divided by YFP intensity (ΔCFP/YFP) scanned with a 458-nm confocal laser. n = 5 larvae per group.
(G & H) Knockdown of 5-HT1b in C4da neurons, but not that in A08n, significantly blocks the effect of ipsapirone on nociceptor-to-SON transmission. The graphs show the ratio of AITC-elicited Max ΔF/F0 in the presence of 10 µM ipsapirone over that in the presence of DMSO (vehicle). This ratio indicates the extent of serotonergic inhibition of AITC-elicited responses in A08n. In the schematic, neurons expressing GCaMP6f and RNAi are shown in green and purple, respectively. An RNAi line against mCherry was used as a negative control. 5-HT1b #1 (B-33418) and 5-HT1b #2 (B-27635) were used to knock down 5-HT1b. (G) n = 18 neurons (9 larvae), 12 neurons (6 larvae), 13 neurons (7 larvae), 17 neurons (9 larvae), and 12 neurons (7 larvae) for mCherry, 5-HT1a, 5-HT1b #1, 5-HT1b #2, and 5-HT7, respectively. (H) n = 8 (5 larvae), 12 (6 larvae), 10 neurons (5 larvae), and 12 neurons (6 larvae) for mCherry, 5-HT1a, 5-HT1b #1, and 5-HT1b #2, respectively.
(I) Schematic model showing that serotonergic neurons modulate nociceptor-to-SON transmission by providing feedback inhibition.