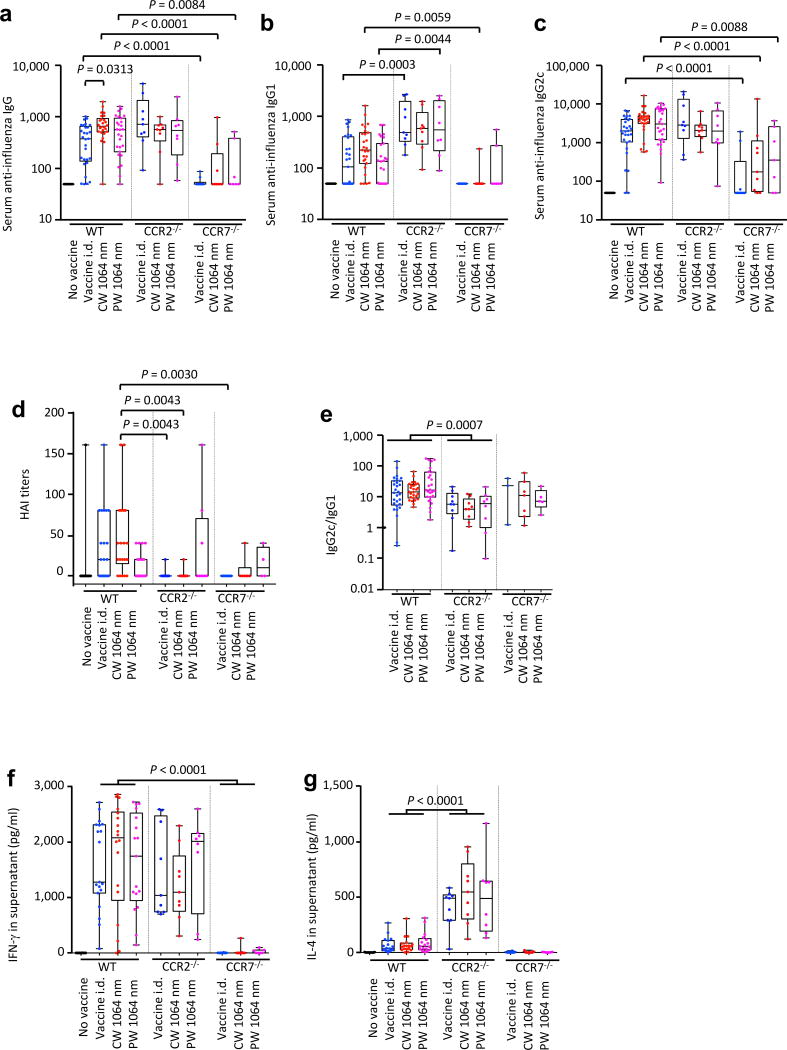
Figure 6. Effect of the laser adjuvant on anti-influenza immune responses in CCR2−/− or CCR7−/− mice.
(a–e) Influenza-specific humoral responses in post-challenge (4 days after challenge). C57BL/6 WT, CCR2−/−, or CCR7−/− mice were vaccinated with 1 µg of inactivated influenza virus (A/PR/8/34) with or without laser illumination and challenged intranasally with live homologous virus 4 weeks after vaccination. Titer of influenza-specific serum IgG subclass was determined by ELISA. (a) IgG, (b) IgG1 and (c) IgG2c titers. (d) HAI titers. (e) IgG2c/IgG1 ratio. All experiments were repeated 3 times and pooled to show results. (f–g) Systemic T-cell responses were measured 4 days after challenge by re-stimulating 1×106 splenocytes with inactivated influenza vaccine antigen for 60 hours. Levels of (f) IFN-γ and (g) IL-4 in splenocyte culture supernatants are shown. Data were analyzed with two-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey's HSD tests. WT data from Fig. 1 are shown for comparison. See the Material and Methods section for strategy used for statistical analysis. Experimental and control groups: (a–c, e) n = 30, 29, 26, 27, 9, 9, 8, 10, 9, 7, (d) 14, 22, 22, 22, 9, 9, 8, 7, 6, 4 (f–g) n = 20, 19, 18, 17, 9, 9, 8, 10, 9, 7 for no vaccine in WT, vaccine i.d. in WT, vaccine i.d. + CW 1064 nm in WT, vaccine i.d. + PW 1064 nm in WT, vaccine i.d. in CCR2−/−, vaccine i.d. + CW 1064 nm in CCR2−/−, vaccine i.d. + PW 1064 nm in CCR2−/−, vaccine i.d. in CCR7−/−, vaccine i.d. + CW 1064 nm in CCR7−/−, vaccine i.d. + PW 1064 nm in CCR7−/−groups, respectively.