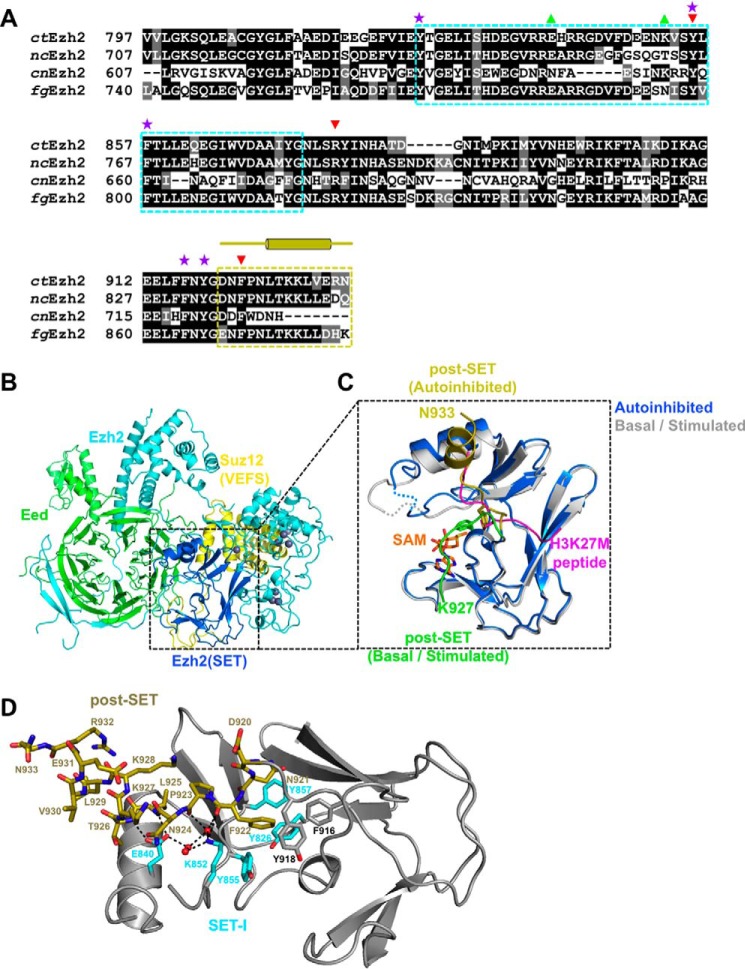
Figure 1.
The autoinhibited conformation of ctPRC2. A, sequence alignment of Ezh2 from fungal species. nc, Neurospora crassa; cn, C. neoformans; fg, F. graminearum. The SET-I (cyan) and post-SET (gold) subdomains are indicated by dotted boxes. Selected residues are designated by symbols as follows: purple stars, aromatic residues from the lysine access channel; green upward triangles, gain-of-function mutations; red downward arrows, loss-of-function mutations. The secondary structures of the post-SET subdomain are also indicated by cylinders (α-helices) and lines (loops) above the sequence alignment. B, overall structure of the apo-ctPRC2 complex. Subunits and domains are color-coded, and zinc ions are shown as gray spheres. C, zoomed-in view of the SET domain of Ezh2 of apo-ctPRC2 aligned with the structure of ctPRC2 in the stimulated state (Protein Data Bank code 5KKL). The post-SET in apo-ctPRC2 (gold) clashes with the substrate peptide (magenta), whereas the same region of ctPRC2 (green) supports SAM and histone substrate binding in the stimulated state. Residue Phe-922 is shown as sticks and would clash with the substrate residue Lys-27 in apo-ctPRC2 but not in the stimulated-state structure. D, intramolecular interactions hold the post-SET and SET-I regions in an autoinhibited conformation. Critical residues of the post-SET (gold) and SET-I (cyan) are labeled. Water molecules are depicted as red spheres. Hydrogen bonds are shown as dashed black lines.