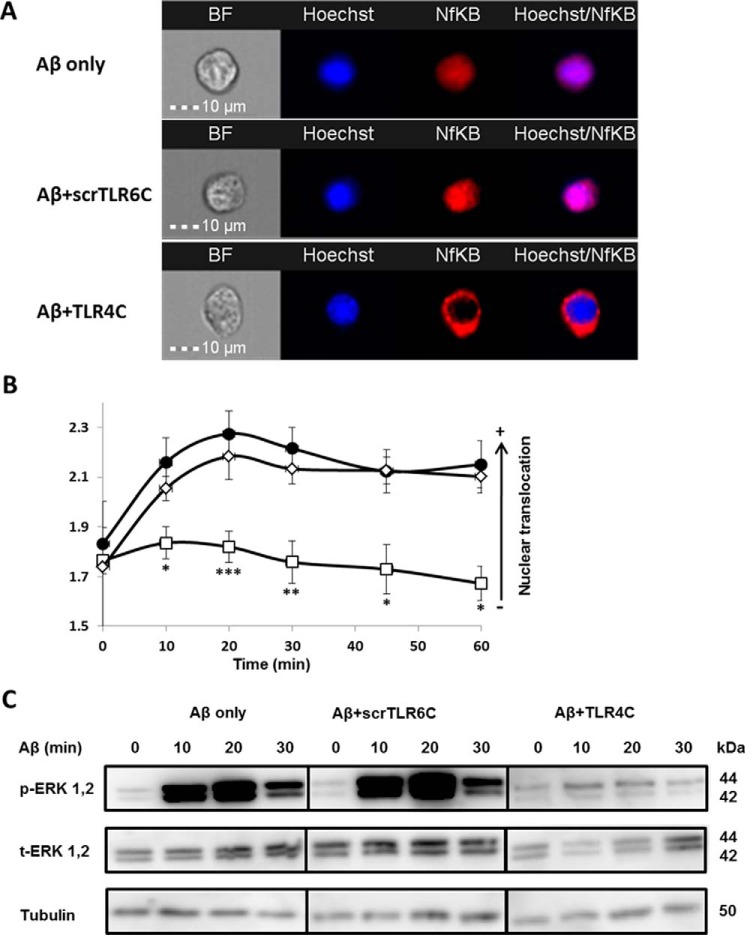
Figure 4.
The TLR4C peptide attenuated TLR4-TLR6 heterodimer downstream signaling of BV2 microglia cells. A and B, the TLR4C peptide inhibits NF-κB translocation to the nucleus upon activation with Aβ. A, representative images of cellular NF-κB staining after 20min in BV2 microglia cells. B, a graphic summary of cellular NF-κB translocation to the nucleus at different time points in BV2 microglia cells with the indicated treatments as observed by fluorescence resonance energy transfer using ImageStreamX. Cells were treatment with 10 μm Aβ (●) for the indicated times after incubation with 20 μm concentrations of either the TLR4C (□) or the scrTLR6C (♢) peptide for 1 h. For labeling of NF-κB, rabbit anti-NF-κB was added (1:50) overnight at 4 °C (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) followed by staining with a secondary anti-rabbit-APC (1:100) for 2 h at room temperature (Biolegend). For nuclear staining, Hoechst was added to the cells (1:1000) for 5 min. Results are the mean ± S.E. of six independent experiments (***, p < 0.005, n ≥ 1300 cells for each experiment). C, the TLR4C peptide inhibits ERK1/2 phosphorylation after activation with Aβ. Shown is a representative image from two independent experiments of ERK1/2 phosphorylation levels in BV2 microglia cells after Aβ exposure. Cells were pretreated for 0.5 h with 20 μm concentrations of the TLR4C peptide, scrTLR6C peptide, or untreated and then washed and incubated with 10 μm Aβ for the indicated times. ERK1/2 phosphorylation levels and total ERK1/2 levels were detected by Western blotting. Equal loading was detected by measuring tubulin.