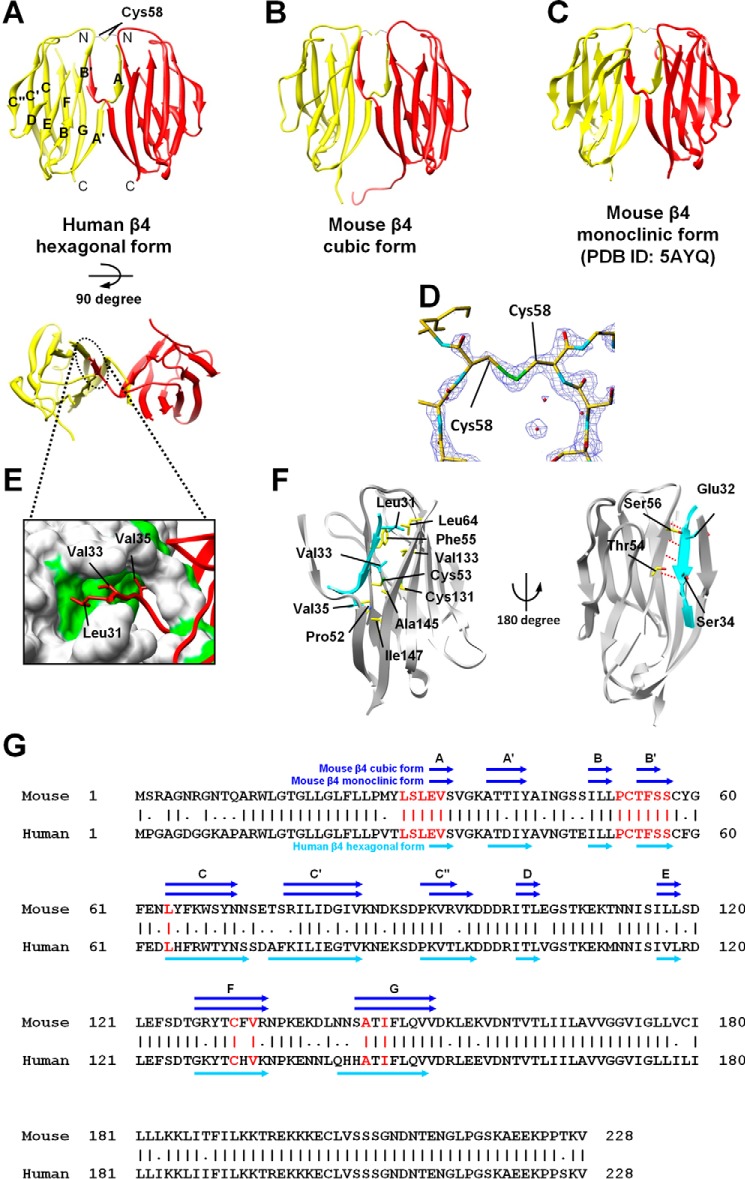
Figure 2.
Structures of the parallel dimer of β4. A–C, ribbon representations of the β4 parallel dimer in which one molecule is colored yellow and the other is red. Shown are a side view (top panel) and top view (bottom panel). Also shown are the human β4 hexagonal form (A), the mouse β4 cubic form (B), and the mouse β4 monoclinic form (C). D, 2Fo-Fc composite omit map (contoured at 1.5 σ) around the intermolecular disulfide bond between the Cys58 residues. E, the intermolecular hydrophobic interactions of the N-terminal segment (the N–N interaction). The surface-exposed hydrophobic residues are colored green. F, detailed views of the N–N interactions. The N-terminal segment of one molecule is colored cyan, and the other molecule is shown by a gray ribbon and a yellow stick model. Hydrogen bonds are shown with dotted red lines. G, amino acid sequences of the mouse and human β4s. The intermolecular interactions (shown in red) are conserved in the human and mouse β4s. The β strands are shown as arrows. Sequence alignment was performed using the Genetyx software (Genetyx Corp., Tokyo, Japan).