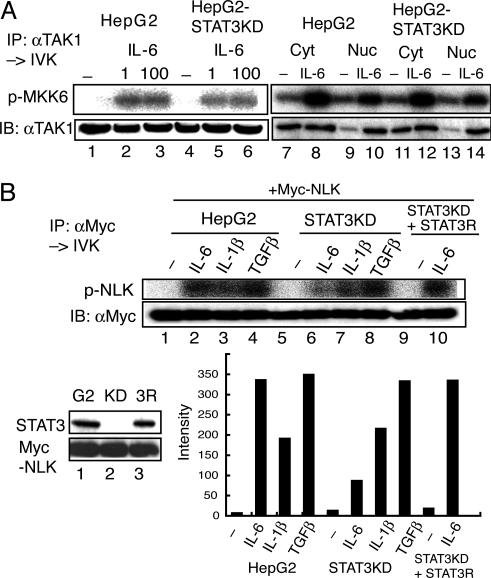
Fig. 4.
STAT3 is required for IL-6-induced NLK activation but not for TAK1 activation. (A) HepG2 and HepG2-STAT3-knockdown (KD) cells were left unstimulated or stimulated with IL-6 at 1 (lanes 2 and 5), 100 (lanes 3 and 6), or 20 (lanes 8, 10, 12, and 14) ng/ml. Endogenous TAK1 from WCE extracts (lanes 1–6), cytosolic extracts (Cyt, lanes 7, 8, 11, and 12) or nuclear extracts (Nuc, lanes 9, 10, 13, and 14) was immunoprecipitated with an anti-TAK1 Ab, and the kinase activity was measured by using MKK6 as the substrate (Upper). (Lower) Immunoblotting with the anti-TAK1 Ab. (B) HepG2 (G2) cells, HepG2-STAT3KD (KD), and HepG2-STAT3KD reconstituted with RNAi-resistant STAT3 (3R) were infected with LV-Myc-NLK. The expression levels of STAT3 and Myc-NLK are shown in Left Lower. These HepG2 and derivative cells expressing Myc-NLK were left unstimulated or stimulated with the indicated cytokines at 20 ng/ml for 10 min. Kinase assay (Upper) and Western blotting analysis (Lower) of the anti-Myc-immunoprecipitates of WCE are shown. The radioactivity level of each band in the kinase assay was quantified with the BAS 5000 Bioimaging analyzer (Fujix, Tokyo). The activity of NLK in the IL-6-stimulated HepG2-STAT3 KD was estimated to be 17.6 ± 7.6% of that of IL-6-stimulated HepG2 cells (n = 4).