Figure 1.
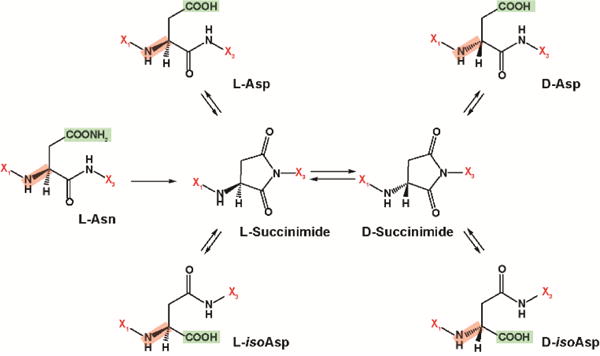
The isomerization pathway and structures for L-aspartic acid (L-Asp), D-aspartic acid (D-Asp), L-isoaspartic acid (L-isoAsp) and D-isoaspartic acid (D-isoAsp). X1 and X3 denote amino acids before and after each specific residue shown. The key -NH2 group was highlighted in red for L- and D-differentiation, and -COOH groups (and -COONH2 for Asn) were highlighted in green to illustrate Asp isomerization.
