Central Illustration. Dose-response relationship of (A) the Plant-based Diet Indices and (B) animal, healthy plant, and less healthy plant foods with CHD incidence.
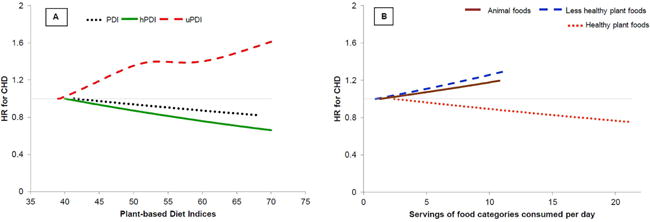
Analysis carried out after combining all three cohorts Adjusted for age, smoking status, physical activity, alcohol intake, multivitamin use, aspirin use, family history of CHD, margarine intake, baseline hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and diabetes, and updated body mass index. Also adjusted for postmenopausal hormone use in NHS & NHS2, and for oral contraceptive use in NHS2. Energy intake was additionally adjusted when analyzing the plant-based diet indices. The three plant-based diet indices were examined in separate models. The three food categories (healthy and less healthy plant foods, and animal foods) were simultaneously included in the same model.
For uPDI, p for test of curvature=0.01 and p for non-linear association<0.001. P for test of curvature for PDI=0.25, for hPDI=0.82, for animal foods=0.58, for healthy plant foods=0.99, and for less healthy plant foods=0.74; P for linearity=0.004 for animal foods, 0.001 for PDI, and <0.001 for hPDI, less healthy plant foods, and healthy plant foods.
Abbreviations: CHD, Coronary Heart Disease; hPDI, Healthful Plant-based Diet Index; PDI, Overall Plant-based Diet Index; uPDI, Unhealthful Plant-based Diet Index
