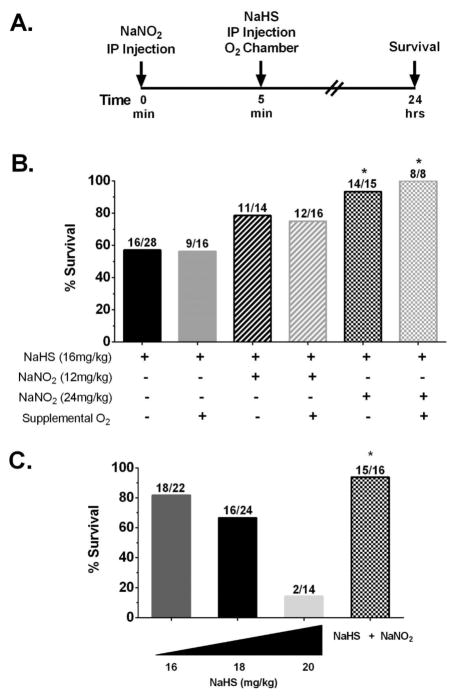
Figure 1.
Prophylactically administered NaNO2 ameliorates NaHS toxicity in mature and juvenile mice. (A) Injection paradigm. (B) Mice (Swiss Webster males, 16–18 weeks of age) were given NaHS in saline (16 mg/kg, ip), and times until death were recorded. The duration of survival (breathing cessation) was measured from the time of the sulfide injection (t = 0). Survival quotients are shown with surviving mice/total mice written above the bar. NaNO2 (12 or 24 mg/kg, ip) was given 5 min prior to NaHS injection. Supplemental oxygen (100% O2) was administered for either 15 min or until death immediately after NaHS injections (* p ≤ 0.05 vs NaHS injection alone). (C) Juvenile mice (Swiss Webster males, 6–8 weeks old) were injected (ip) with either 16, 18, or 20 mg/kg NaHS, and survival was recorded as for adults. In addition, 24 mg/kg NaNO2 was given 5 min before 18 mg/kg NaHS (* p ≤ 0.05 vs 18 mg/kg NaHS injection).