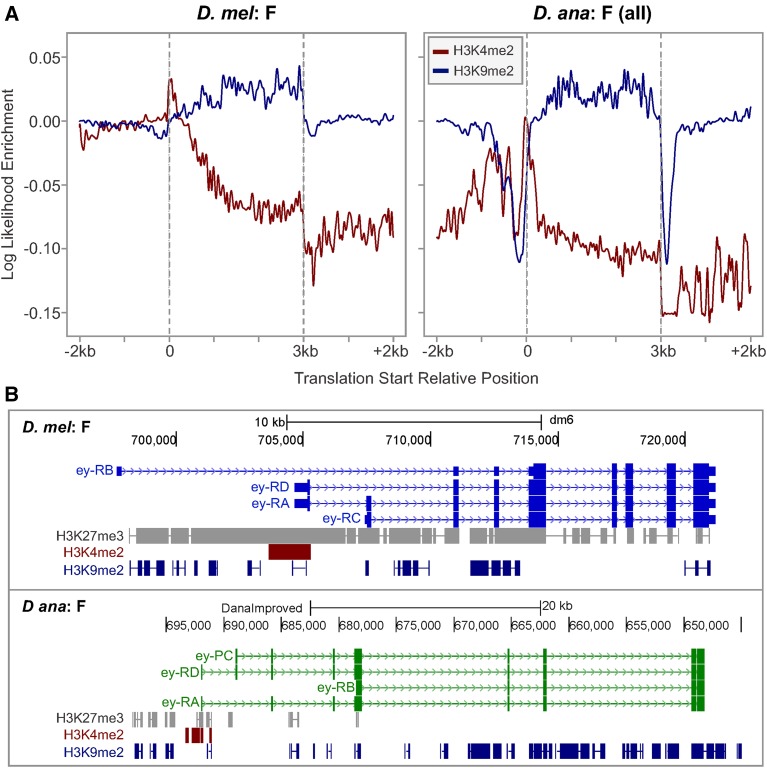
Figure 7.
Histone modification profiles for D. ananassae and D. melanogaster F-element genes at the third instar larval stage of development. (A) Metagene analysis shows that the region surrounding the 5′ end of F-element genes is enriched in H3K4me2 while the body of the coding span is enriched in H3K9me2. The values in the y-axis within each metagene plot correspond to the log-likelihood ratio between each ChIP sample and input control (assuming a dynamic Poisson model) as determined by MACS2. (B) Differences in the H3K27me3 enrichment patterns for the D. melanogaster ey gene and its ortholog in D. ananassae. The entire coding span of the ey gene is enriched in H3K27me3 in D. melanogaster (top) (for the D. melanogaster gene models, the thick boxes denote the coding exons and the thin boxes denote the untranslated regions). By contrast, only the region surrounding the 5′ end of the ey ortholog in D. ananassae shows H3K27me3 enrichment. The 5′ ends of the A and D isoforms of ey shows enrichment of H3K4me2 and H3K27me3 in both D. melanogaster and D. ananassae. These bivalent domains suggest that these two isoforms of ey are poised for activation at the third instar larval stage of development in both species.