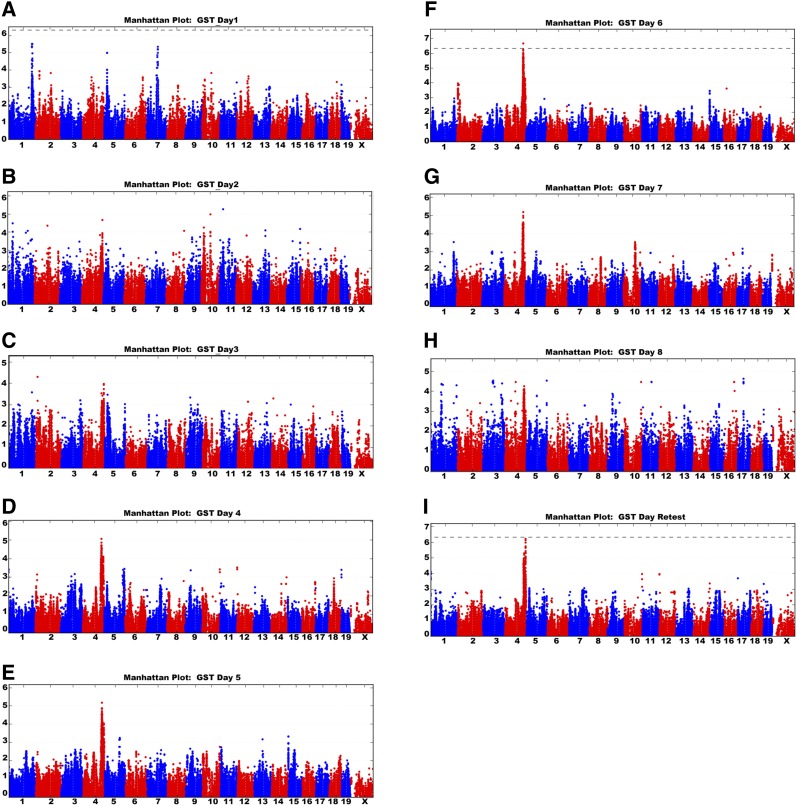
Figure 3.
Genome-wide association results in the HMDP demonstrate a shift in seizure susceptibility over repeated-flurothyl-induced seizures. Manhattan plots for the seizure susceptibility associations over repeated seizures. (A) Acute seizure susceptibility associated with multiple suggestive associations >10−4 including chromosomes 1, 5, and 7. (B–E) Manhattan plots of day 2 to day 5 GST scores variance show a progression of associations to Distal Chromosome 4. (F) By the 6th induction seizure (day 6), associations exceeding genome-wide significance are detected on distal chromosome 4 near 139 Mb (GRCm38). (G and H) Manhattan plots of day 7 and day 8 GST variance. (I) Distal chromosome 4 associations persist until a retest seizure (given 4 wk after the induction period) with the five most significant SNP associations occurring in Camta1 (151 Mb). Dotted line represents genome-wide significance (P < 4.4 × 10−6).