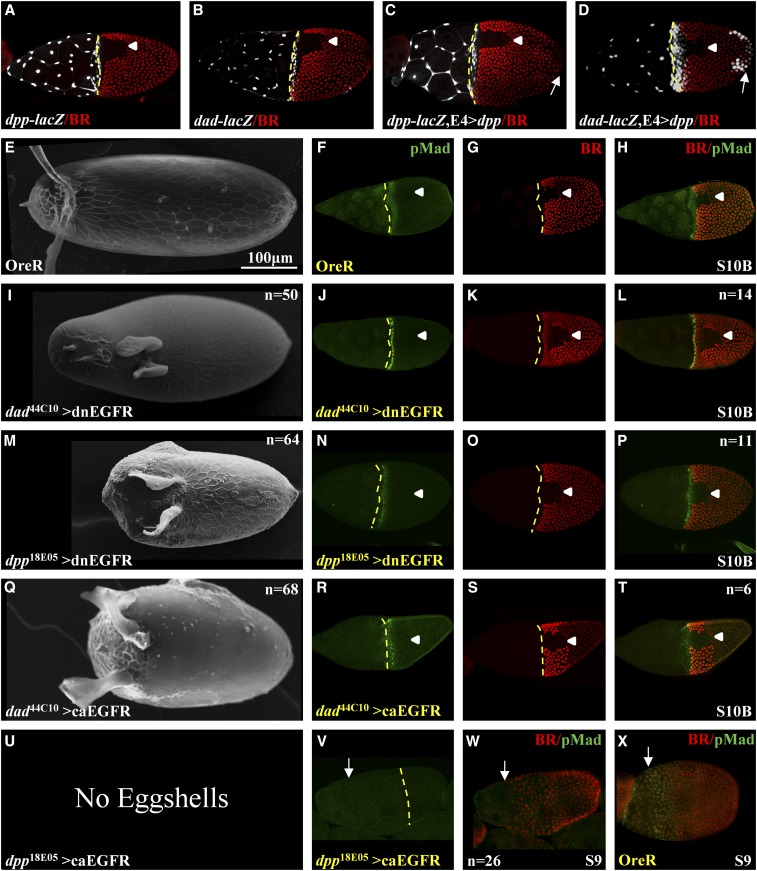
Figure 3.
Genetic perturbations using dad44C10 and dpp18E05 FlyLight lines. (A and B) β-galactosidase expression patterns of dad44C10 and dpp18E05 lines in the anterior and stretched cells domains (dad-lacZ and dpp-lacZ). (C and D) Expression of dpp in the posterior end (E4>dpp) induces ectopic expression of β-galactosidase expression in the posterior domain in dad-lacZ but not in dpp-lacZ (denoted by a white arrow). BR staining is used as a spatial marker. Arrowheads denote the dorsal midline. Broken yellow lines denote the anterior boundary of the oocyte. (E–H) OreR (E) eggshell, (F) pMad (green), (G) BR (red), and (H) merge. (I–L) dad44C10 driving the expression of a dnEGFR: (I) eggshell, (J) pMad, (K) BR, and (L) merge. (M–P) dpp18E05 driving the expression of a dnEGFR: (M) eggshell, (N) pMad, (O) BR, and (P) merge. (Q–T) dad44C10 driving the expression of a caEGFR: (Q) eggshell, (R) pMad, (S) BR, and (T) merge. (U–X) dpp18E05 driving the expression of caEGFR: (U) no eggshell, (V) pMad [↓ denoted the anterior boundary of the future oocyte-associated follicle cells, also in (W)], and (W) merged image of pMad and BR (a separate BR image is not shown). (X) For comparison, we included the wild-type (OreR) merged BR/pMad image at S9. We note that oogenesis stopped at stage 9 in the dpp18E05 > caEGFR background. No pMad is present in egg chambers. Egg chambers’ developmental stages are denoted. All images are a dorsal view and anterior is to the left.