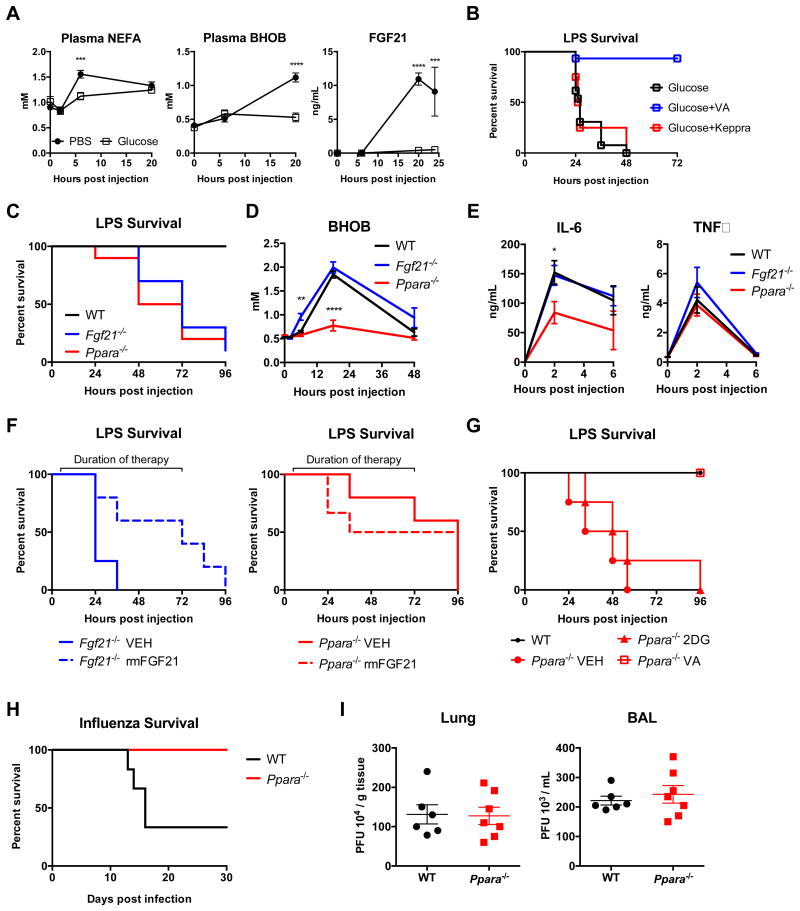
Figure 6. Role of ketogenic program in surviving bacterial, but not viral inflammation.
(A) Plasma nonesterified fatty acids (NEFA), beta-hydroxybutyrate (BHOB), and fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) after LPS, with treatment with IP PBS or glucose. n=10/group.
(B) Survival after 8 mg/kg IP LPS and treatment with glucose. Mice were treated with vehicle, valproic acid (VA) or levetiracetam (Keppra) starting 6 hours after LPS. p<0.0001 for Glucose+VA vs Glucose and Glucose+VA vs Glucose+Keppra. n=15 Glucose, n=15 Glucose+VA, n=4 Glucose+Keppra.
(C) Survival after 12.5 mg/kg IP LPS in B6 WT, Fgf21-/- and Ppara-/- mice. n=10/group. p<0.0001 for WT vs Fgf21-/-; p=0.0003 for WT vs Ppara-/-.
(D) Plasma BHOB after 12.5 mg/kg IP LPS in WT, Fgf21-/- and Ppara-/- mice. n=4-6/group.
(E) Plasma TNFα and IL-6 in B6 WT, Fgf21-/-, and Ppara-/- mice after LPS. n=5/group *p<0.05.
(F) Survival after 12.5 mg/kg IP LPS in Fgf21-/- and Ppara-/- mice, treated with i.v. 5 ng recombinant mouse FGF21 (rmFGF21) twice daily starting 6 hours after LPS injection. n=5-6/group. p=0.0491 Fgf21-/- VEH vs Fgf21-/- rmFGF21. p=0.5767 Ppara-/- VEH vs Ppara-/- rmFGF21.
(G) Survival after 8 mg/kg IP LPS in B6 WT and Ppara-/- mice. 2DG treatment was initiated one hour after LPS. Valproic acid (VA) was initiated 6 hours after LPS. n=4-5/group. p=0.0177 Ppara-/- VEH vs Ppara-/- VA.
(H-I) WT and Ppara-/- mice were infected with 400 PFU of influenza virus.
(H) Survival after influenza infection. p=0.0074 WT n=6, Ppara-/- n=8, representative of three independent experiments.
(I) Lung and BAL viral load 5 days post-infection. n=6-7/group.
Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. See also Figures S6 and S7.