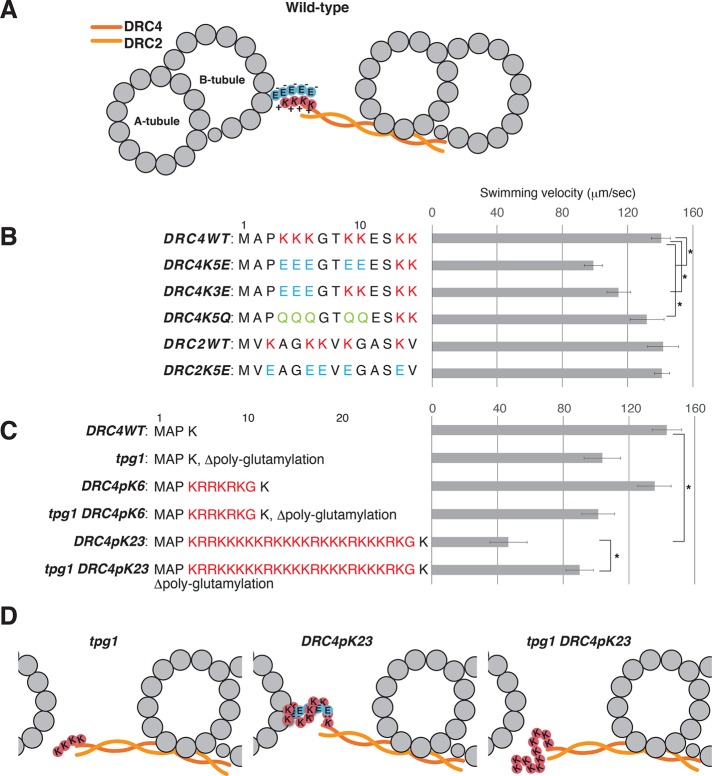
FIGURE 3:
Effects of replacement and addition of Lys residues on flagellar motility. (A) Schematic diagram of the DMT and the N-DRC, showing the possible electrostatic interaction between the polyglutamate chain (circled E) extending from the B-tubule and the polylysine chain (circled K) on the DRC4. The coiled-coil complex of DRC2 and DRC4 is indicated by orange wavy lines. (B, C) Swimming velocities of DRC4 and DRC2 mutants. Residue replacements and additions are shown next to the strain names. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (p < 0.01). The p values were calculated using Student’s t test. Means ± SEM for the mean swimming velocities were calculated from 20 cells. (B) Lys residues on DRC4 and DRC2 were replaced with either Glu or Gln. (C) A total of 6 or 23 residues of Lys and Arg residues were inserted after the Pro-3 of DRC4. (D) Schematic diagrams of the interaction between DRC4 and the B-tubule. In tpg1, the interaction between the poly-Lys on DRC4 and the B-tubule is abolished. In DRC4 pK23, the hyper-poly-Lys peptide on DRC4 forms an excessively strong cross-bridge with polyglutamylated tubulin on the B-tubule.