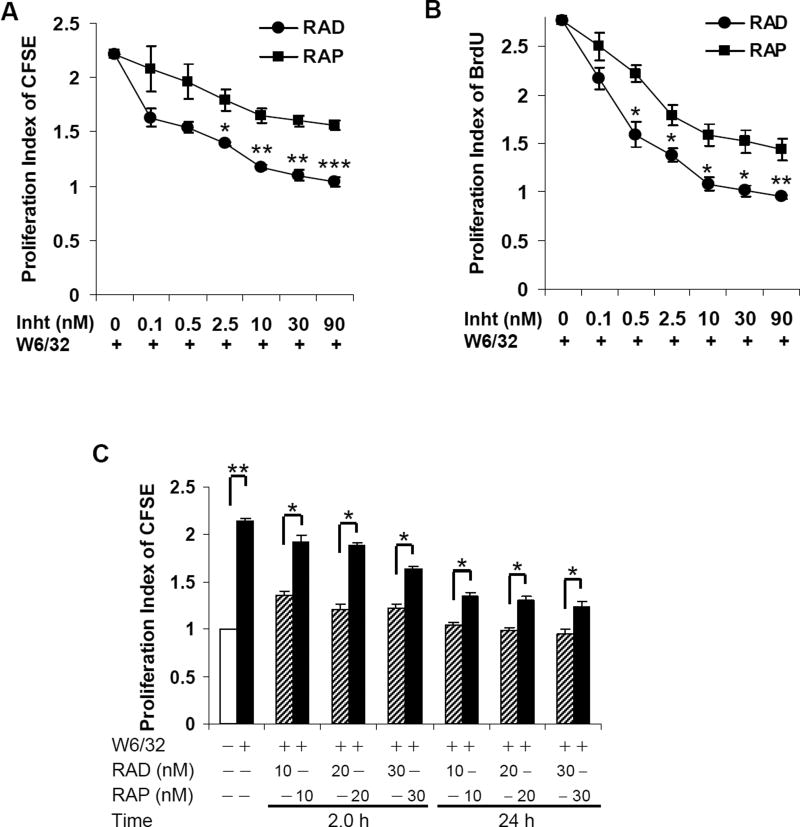
Fig. 1. Everolimus inhibits HLA I-stimulated cell proliferation more potent than sirolimus.
Quiescent EC were pretreated with different concentrations of everolimus or sirolimus for 24hr and then stimulated with 1.0µg/ml anti-HLA I mAb for 48hr. Proliferation was determined by A, CFSE dilution or B, BrdU incorporation. For CFSE dilution, EC proliferation was measured by flow cytometry and analyzed by Modfit LT software. Cell proliferation was calculated using the Proliferation Wizard Model. The proliferation index (PI) is the sum of the cells in all generations divided by the computed number of original parent cells present at the start of the experiment. For BrdU incorporation, proliferation index is presented as fold increase in the percent of cells positive for BrdU normalized to untreated control. C EC were pretreated with 10, 20, or 30nM of everolimus or sirolimus for 2 or 24hr, and proliferation in response to HLA I mAb was measured by CFSE dilution. *p<0.05, **p<0.01, and ***p<0.001 were analyzed by one way ANOVA with Fisher’s LSD. Data represent at least three independent experiments. HAEC used in these experiments include CAR, CAS, and 5555.