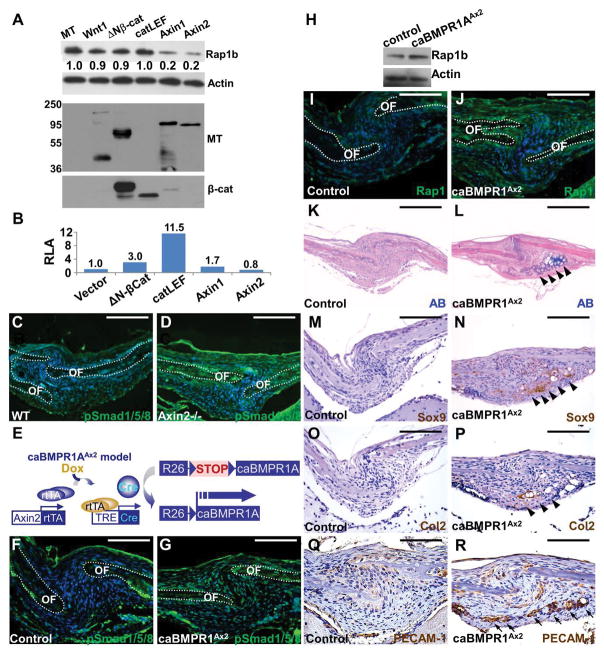
Figure 2.
Rap1b is regulated by Axin2-BMP signaling axis. (A–B) Modulation of Rap1b by Axin2 is independent of β-catenin-mediated transcription. (A) Immunoblot analysis examines the Rap1b level affected by overexpression of myc-tag (MT), Wnt1, ΔNβ-catenin, catCLEF, Axin1 or Axin2, in C3H10T1/2 cells. Actin level is used as a loading control. The expression of transfected genes is shown by immunoblotting of MT and β-catenin. (B) Relative luciferase activity (RLA) examines the β-catenin and Lef/Tcf-dependent transcription of a TOPFlash reporter affected by Wnt signaling effectors. (C–D) Immunostaining of phosphorylated Smad1/5/8 (pSmad1/5/8) shows enhanced canonical BMP signaling in the sagittal suture of Axin2−/−. (E) Diagrams illustrate the creation of caBMPR1AAx2 model where a constitutive active form of BMPR1A is expressed in the Axin2-expressing stem cells within the skeletogenic mesenchyme upon Dox treatment. (F–R) Stimulation of BMP signaling activates Rap1b and promotes chondrogenic fate in the suture mesenchyme at P3. Immunostaining (F–G, I–J) and immunoblotting (H) examines alterations of canonical BMP signaling (F–G) and Rap1b expression (H–J) in the caBMPR1AAx2 sagittal suture. OF, osteogenic front. Actin level is used as a loading control for immunoblot analysis. Alcian blue (AB) staining (K–L), and Sox9, type 2 collagen (Col2) and PECAM-1 immunostaining analyses (M–R) reveal evidence of ectopic chondrogenesis (arrowheads) and vascular invasion positive for endothelial cells (arrows) caused by constitutive activation of BMPR1A in the P3 sagittal suture. Sections are counterstained by DAPI (C–D, F–G, I–J), nuclear fast red (K–L) and hematoxylin (M–R). Images are representatives of three independent experiments. Scale bars, 100 μm (C–D, F–G, I–J, Q–R); 200 μm (K–P).