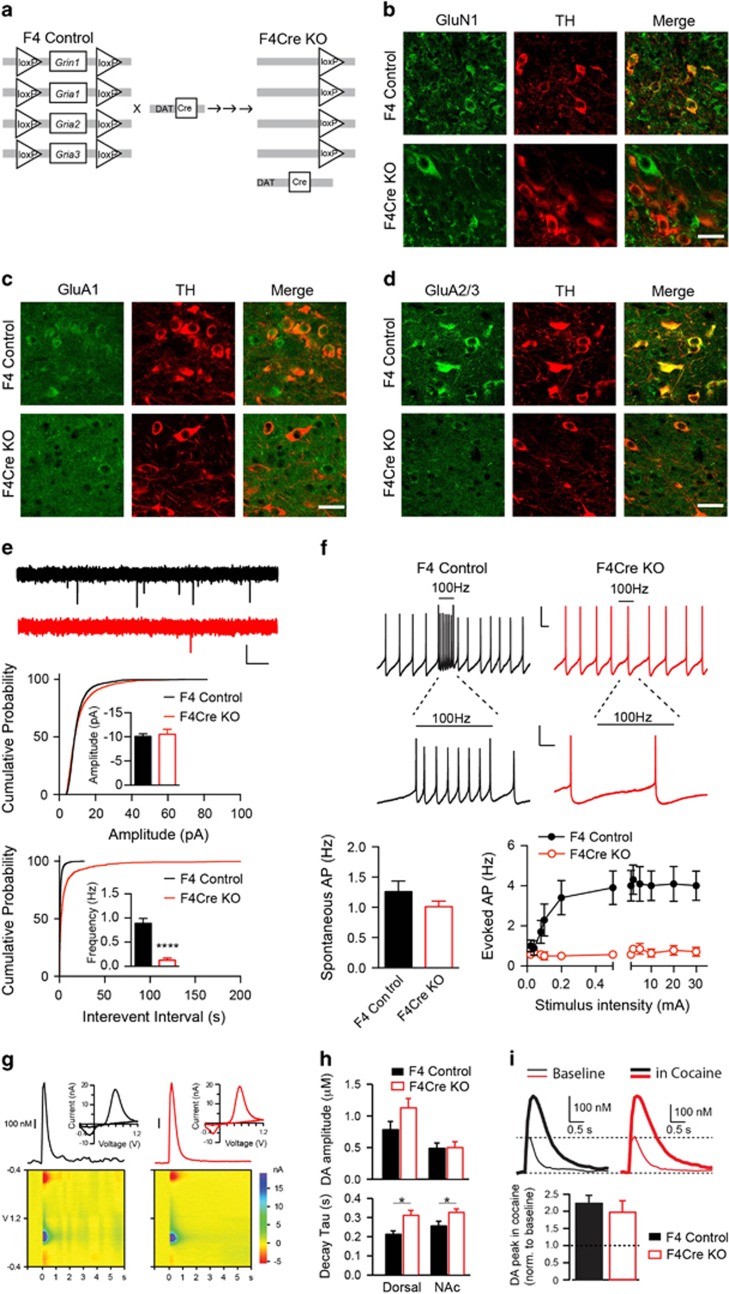
Figure 1.
Generation and characterization of F4 and F4Cre mouse lines. (a) Schematic of Grin1 and Gria1-3 alleles in F4 and F4Cre mice. The DAT-Cre mouse line was crossed with a Gria1-3fl/flGrin1fl/fl (F4) line to generate Cre-positive Gria1-3+/flGrin1+/fl mice that were then crossed with Gria1-3fl/flGrin1fl/fl mice to produce the conditional knockout mouse line (F4Cre). (b–d) High-power (× 40) images of staining for GluN1 and TH (b) for GluA1 and TH (c) and for GluA2/3 and TH (d) in ventral tegmental area (VTA) neurons. Scale bar: 25 μm. (e) mEPSC frequency but not amplitude in VTA DA neurons was strongly reduced in F4Cre/tdTomato mice (Cre/tdTomato, n=13, F4Cre/tdTomato, n=15). Scale bar: 10 pA, 0.5 s. The breeding scheme for all electrophysiological experiments is shown in Supplementary Figure S1B. (f) Stimulation-induced VTA DA neuron firing evoked by 100 Hz electrical stimulation (for 1 s) was lost in F4Cre/tdTomato mice (sample traces from stimulation at 0.5 mA). Scale bars: 25 mV/500 ms (top), 25 mV/200 ms (middle). (g) Representative DA transients (top) evoked by single pulse electrical stimulation in the dorsal striatum of brain slices from F4 (black) and F4Cre mice (red) measured by fast-scan cyclic voltammetry. Color plot voltammograms (bottom) and current–voltage plots (insets) showing the characteristic oxidation and reduction peaks for DA. (h) DA concentration and clearance properties of transients recorded in the dorsal striatum (dorsal, F4, n=7, F4Cre, n=6) and nucleus accumbens (NAc, F4, n=13, F4Cre, n=13) of F4 and F4Cre mice. (i) Representative DA transients evoked by single pulse electrical stimulation before (thin) and after cocaine (1 μM, thick) 30- min application in the NAc of F4 (black, n=3) and F4Cre mice (red, n=3) (*P<0.05, ****P<0.0001 and P⩾0.05, no significance). All data were presented as mean±s.e.m. DA, dopamine; EPSC, excitatory postsynaptic current.