Figure 4.
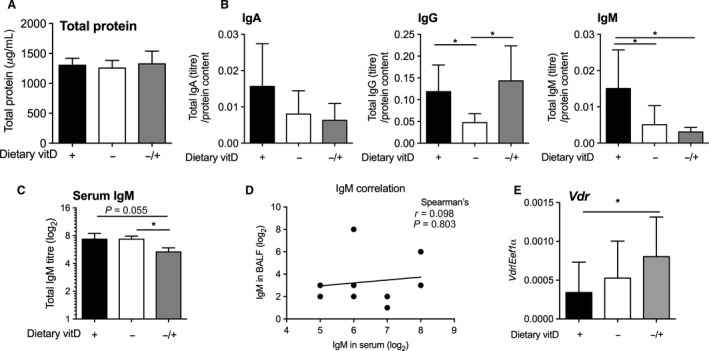
Total protein and antibody isotypes (IgA, IgG, and IgM) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid, serum IgM levels, and Vdr mRNA in the lungs. Female BALB/c mice (dams) were fed vitamin D‐supplemented (+) or vitamin D‐nonsupplemented (−) diets from 3 weeks of age and used to produce offspring. A subgroup of vitamin D‐deficient offspring was fed a vitamin D‐supplemented diet from 8 weeks of age (−/+). In (A), total protein levels (12–17 mice per treatment), and in (B), total IgA, IgG, and IgM levels (9–10 mice per treatment; *P < 0.05, two‐way t test) in the BALF (relative to BALF protein levels) of these mice at 12 weeks of age. In (C), total IgM levels in the sera of mice at 12 weeks of age (three mice per treatment; *P < 0.05; two‐way t test). In (D), correlation of IgM levels in BALF and serum (Spearman's: n = 9). In (E), mRNA levels of the vitamin D receptor (Vdr) in the lungs are shown relative to the house‐keeping gene Eef1α (8‐10 mice per treatment; *P < 0.05; two‐way t test). Data are shown as mean + SD.
