Fig. 3.
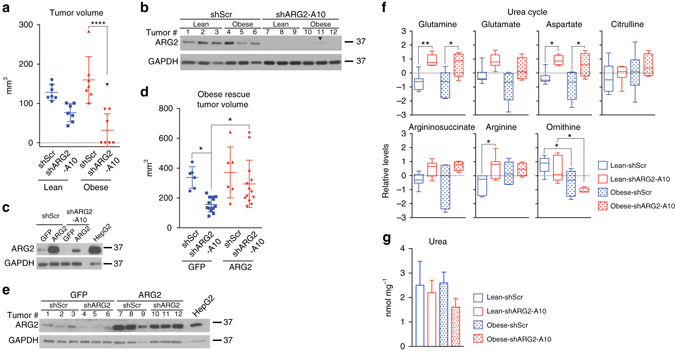
ARG2 is essential for human PDA growth particularly in the obese. a Volumes of orthotopic PDA tumors derived from AsPC1-shScr and AspC1-shARG2 cells, injected (105 cells) into lean or obese 12–14 week old male Rag1 −/− mice and grown for 6 weeks (n = 7 except for obese-shARG2, n = 8). The black data point indicates an outlier AspC1-shARG2 tumor not included in the statistics, due to re-expression of ARG2. b Immunoblots for ARG2 in tumors from a. Arrowhead indicates outlier in a. c Immunoblots for ARG2 in AsPC1-shScr and AsPC1-shARG2 cells expressing GFP or shRNA-resistant human ARG2. d Volumes of orthotopic PDA tumors from cells in c, grown in obese 27-week old male Rag1 −/− mice for 4 weeks (500,000 cells per mouse, n = 6 for shScr groups and n = 13 for shARG2 groups). Data represent two independent experiments. e Immunoblots for ARG2 from tumors in d. f Relative metabolite levels in PDA tumors from a (n = 7, except for Obese-shARG2, n = 4). Box plots represent medians ± 10-90 percentile. g Urea levels in tumors from f measured by urea assay kit. In a, d, g, data indicate the mean ± s.d. *P ≤ 0.05, **P ≤ 0.01, ****P ≤ 0.0001, by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey test in a, d, f
