Figure 4.
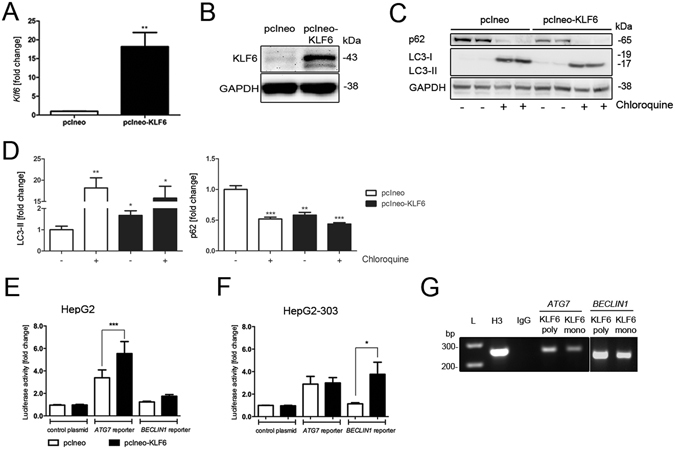
KLF6 transcriptionally activates autophagy-related genes in a p53-dependent manner. Transfection with the KLF6-expression vector pcIneo-KLF6 induced KLF6 mRNA (A) and protein (B) expression. KLF6-over-expression induces autophagy in HepG2 cells as assessed by LC3 Western blotting (C) and quantification of LC3-II-bands normalized to loading control GAPDH (D; fold change versus control shown as mean ± SEM of n = 3 independent cell culture experiments; full length Western blot images are given in Supplementary information.). Autophagic flux was assessed by LC3-II and p62 Western blotting in HepG2 and pcIneo-KLF6 transfected cells in absence (−) or presence ( + ) of 100 µM chloroquine for 24 h ((C) shows representative Western blot images, (D) shows fold change versus control, shown as mean ± SEM of n = 3 independent experiments). Activation of the ATG7 and BECLIN1 promoter was quantified by luciferase activity in a co-transfection experiment of pcIneo-KLF6 with specific promoter reporter luciferase plasmids in HepG2 (E) and in p53-deficient HepG2-303 cells (F). The interaction of KLF6 with the ATG7 and BECLIN1 promoter containing putative KLF6-binding sites was confirmed by chromosomal immunoprecipitation (ChIP) in HepG2 cells (G) using two different KLF6 antibodies, IgG as negative controls, Histone-H3 antibody was used as a positive control for ChIP; full length images of agarose gels are given in Supplementary information.
