Figure 7. KPAF3‐bound RNA is resistant to 3′–5′ degradation by the MPsome.
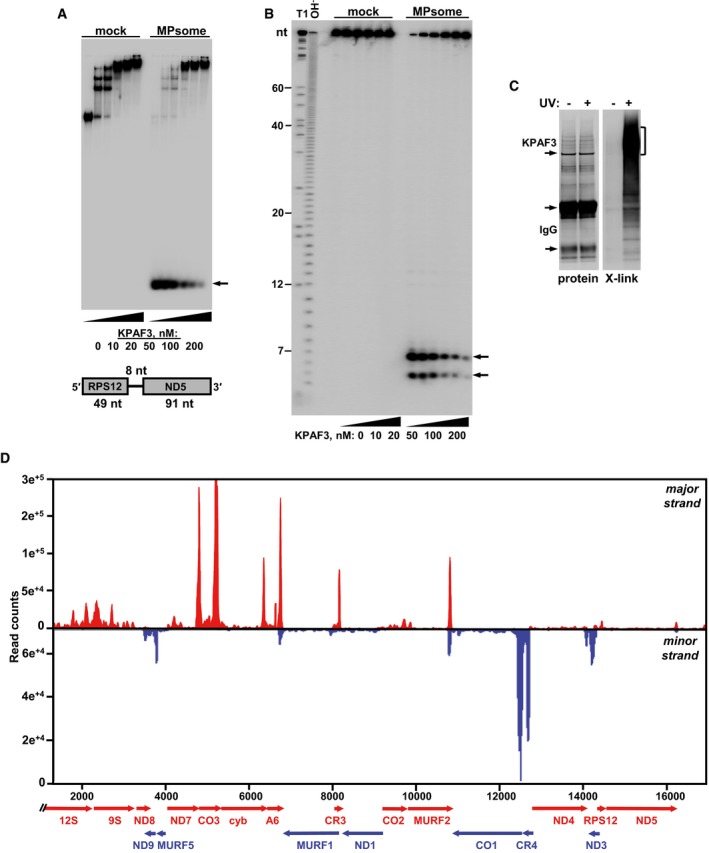
- Electrophoretic mobility shift assay. Increasing amounts of recombinant KPAF3 were incubated with 5′‐radiolabeled RNA in the absence (mock) or presence (MPsome) of tandem affinity‐purified DSS1 exonuclease. Reactions were separated on 7% Tris‐borate native PAGE. Degradation products are indicated by arrows.
- Analysis of RNA degradation patterns. Same reaction products as in (A) were deproteinized and separated on high‐resolution 15% polyacrylamide/8 M urea gel. T1, RNA was digested with G‐specific RNase T1. OH−, alkaline ladder.
- Isolation of in vivo RNA‐KPAF3 crosslinks. KPAF3‐TAP fusion protein was affinity purified from parasites subjected to UV‐irradiation (+) or mock‐treated (−). Final fractions were subjected to partial RNase I digestion, and RNA fragments covalently bound to the protein were radiolabeled. Upon separation on SDS–PAGE, RNA‐protein crosslinks were transferred onto nitrocellulose membrane. Protein patterns were visualized by Sypro Ruby staining (left panel) and RNA‐protein crosslinks by exposure to phosphor storage screen (right panel). RNA was eluted from areas indicated by brackets, converted into barcoded libraries, and sequenced.
- In vivo positioning of KPAF3 binding sites. Crosslinked fragments were mapped to gene‐containing region of the maxicircle. Annotated mitochondrial transcripts encoded on major strand are indicated by red arrows, and those on minor strand are delineated by blue arrows.
Source data are available online for this figure.
