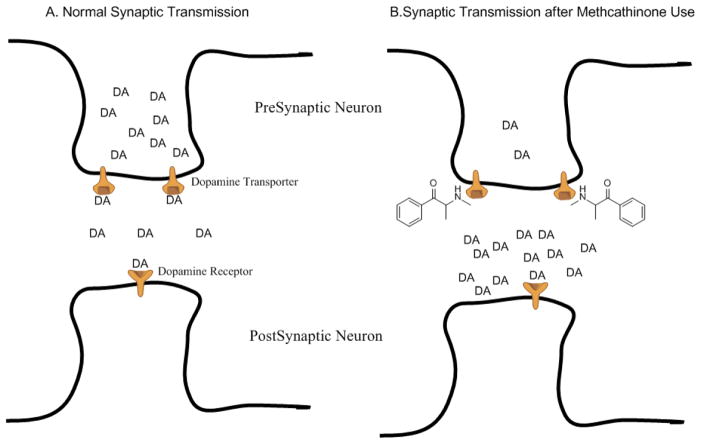
Figure 3.
Simplified schematic of synaptic neurotransmission for the endogenous monoamine dopamine (DA). Panel A shows that under normal (non-drug) conditions, DA is released from the presynaptic neuron into the synaptic cleft where DA can bind to post-synaptic dopamine receptors on the postsynaptic neuron to promulgate neurotransmission. DA can also bind to the dopamine transporter located on the presynaptic neuron and be translocated back into the presynaptic neuron for repackaging and subsequent release. Dopamine uptake by the dopamine transporter is the primary mechanism of terminating the DA-mediated neurotransmission. Panel B shows that under conditions of methcathinone use, there is an increased concentration of DA in the synaptic cleft that results in increased activation of post-synaptic dopamine receptors. Furthermore, methcathinone is a substrate for the dopamine transporter, blocking the ability of DA to bind to the transporter, and thus reducing one of the main mechanisms of dopaminergic neurotransmission termination.