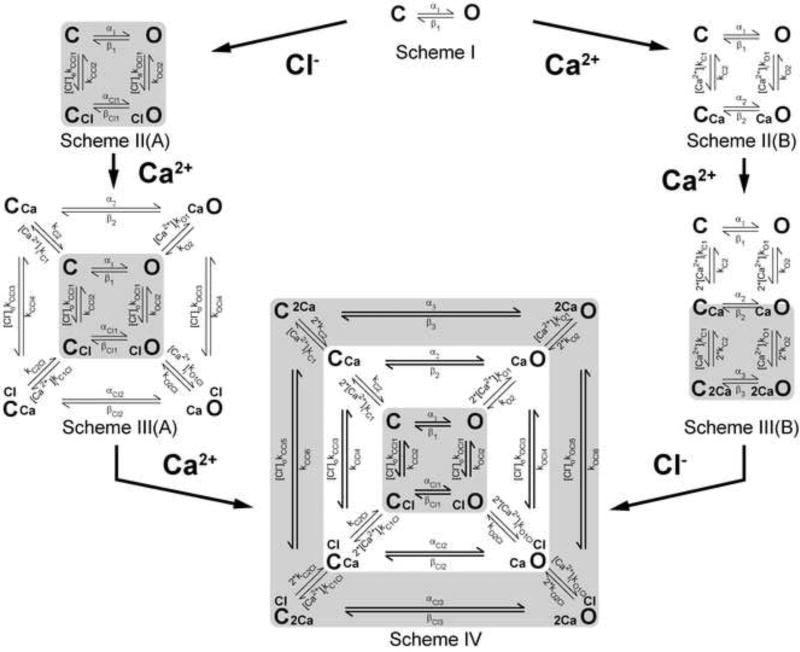
Fig 4. Kinetic model employed to explain the Vm, Ca2+, and Cl− contributions to TMEM16A gating.
Scheme I represents Vm-dependent transitions in the absence of intracellular Ca2+ and external Cl−. C and O are closed and open states, and α1 and β1 are Vm-dependent rate constants. Scheme II(A) represents the transitions in the presence of one external Cl− when [Ca2+]i =0. [Cl−]okCCl1 and [Cl−]okOCl1 are rate constants controlling Cl− association to C and O configurations, while kCCl2, kOCl2 rate constants control Cl− dissociation. Scheme III(A) results after binding of one Ca2+ to states represented in Scheme II(A). The [Ca2+]ikO1, [Ca2+]ikO1Cl, [Ca2+]ikC1Cl and [Ca2+]ikC1 are Ca2+ association rate constants while kO2, kO2Cl, kC2Cl and kC1 are Ca2+ dissociation rate constants. The subscript Cl indicates rate constants associated with Cl−-occupied transitions. Scheme II(B) represents transitions resulting after binding of one intracellular Ca2+ to C and O states depicted in Scheme I. [Ca2+]ikC1, [Ca2+]ikO1 are rate constants controlling Ca2+ association to C and O configurations, while kC2, kO2 rate constants control Ca2+ dissociation. Scheme III(B) represents the transitions resulting after binding of an additional Ca2+ to states shown in Scheme II(B). Association and dissociation of the second Ca2+ was assumed to be same as for the first Ca2+ binding reaction. Scheme IV results after binding of an additional Ca2+ to states shown in Scheme III(A). The association and dissociation rate constants were the same as that for the first Ca2+ binding (left pathway). Alternatively, Scheme IV could be achieved after binding of one external Cl− to states shown in Scheme III(B) with forward rate constants [Cl−]okCCl5, [Cl−]o kCCl3, [Cl−]okCCl1, [Cl−]okOCl1, [Cl−]okOCl3 and [Cl−]okOCl5 and backward rate constants kCCl6, kCCl4, kCCl2, kOCl2, kOCl4 and kOCl6. Concentric kinetic cycles with states connected by wider arrows indicate cycles that did not satisfy microscopic reversibility. Table 2A shows the Equations for each rate constant.