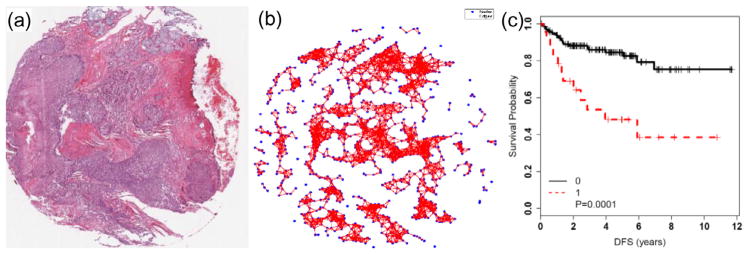
Fig. 2.
Examples of domain agnostic and domain inspired handcrafted features for disease characterization and outcome prediction. An example of domain agnostic cell cluster graph features (b) to capture the spatial architecture of nuclei in p16 + oropharyngeal cancers (a). These CCG features were shown to predict progression (Lewis et al., 2014) in these cancers more accurately than T-stage and lymph node status (c).