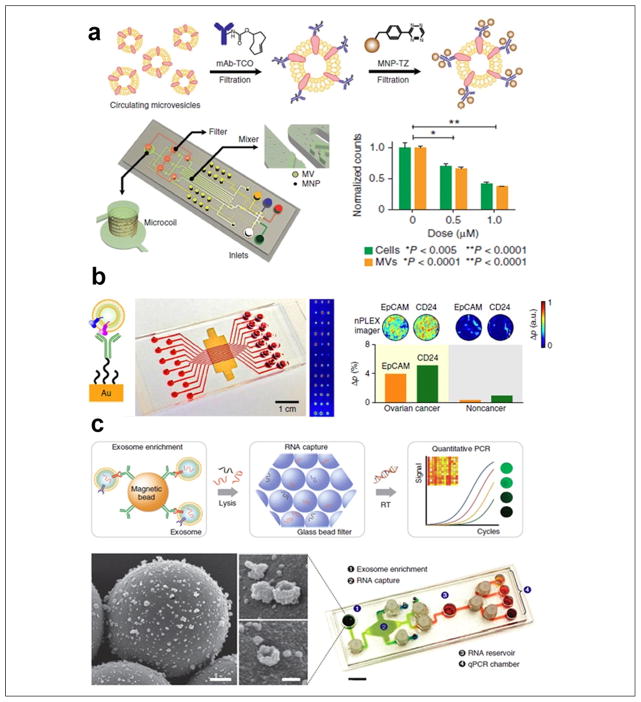
Figure 4.
Microfluidic exosome molecular profiling for monitoring of disease and treatment. (a) μNMR chip with two-step labeling of target proteins on MVs using magnetic nanoparticles. The μNMR microfluidic system is designed to monitor TMZ drug treatment responses for patients with glioblastoma, as MV numbers decrease in proportion to drug concentration. (b) The nPLEX chip evaluated ascites-derived exosomes from ovarian cancer and noncancer patients. Cancer exosomes were captured on EpCAM and CD24-specific sensor sites, which led to intensity changes in the transmitted light (left scheme of principle). The nPLEX chip was integrated with a multichannel microfluidic cell for independent and parallel analyses. Transmission intensities of 12 × 3 nanohole arrays can be measured simultaneously using the imaging setup. (c) The microfluidic iMER chip was developed to integrate (1) capture of cancer exosomes in serum with magnetic microbeads containing affinity ligands, (2) immunoenrichment of exosomal population and lysing for flowing through a glass bead filter and RNA extraction, and (3) elution and reverse transcription for real-time amplification and quantitation. SEM image scale bars are 500 nm, 100 nm (inset). The device has been used for analyzing mRNA levels of drug resistance markers DNA ethyltransferase (MGMT) and alkylpurine-DNA-N-glycosylase (APNG) in enriched tumor exosomes obtained from blood. (Figures are adapted with permission from Nature Publishing Group.)