Figure 1. Bioinformatic analysis of Poldip2.
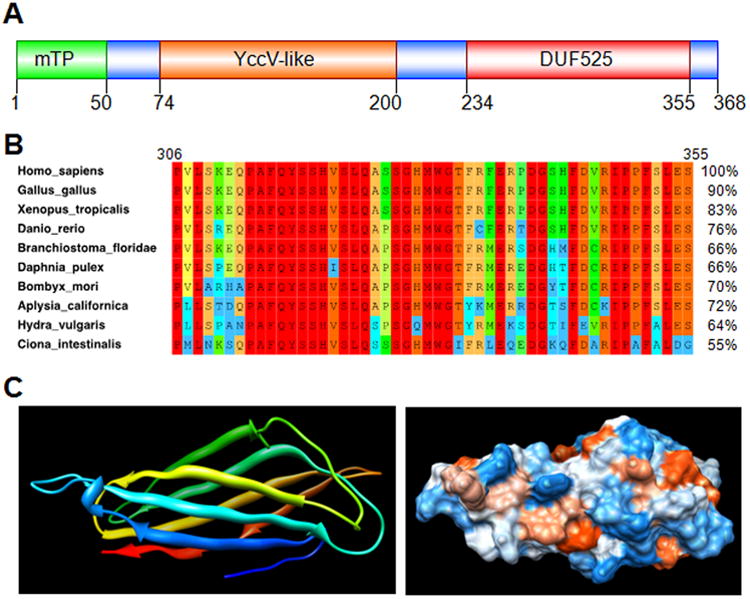
The entire human Poldip2 protein sequence (368 residues, NCBI accession number NP_056399.1) was used to search databases. A. Two domains were returned from the NCBI conserved domains database: the C-terminal DUF525domain, better conserved (E = 4.5e-32) than the upstream YccV-like domain (E = 1.3e-12). The N-terminus is predicted to be a cleavable mitochondrial targeting peptide (mTP) with near certainty, according to online software, such as TargetP,37, 38 Mitoprot39 and MitoFates.40 A BLAST search of the NCBI non-redundant protein sequences database returned about 600 homologous sequences from Eukaryotes (E < 1e-26). Each organism appeared to have a single gene homologous to Poldip2, suggesting that these hits are orthologs. Remarkably, BLAST detected no fungus, plant or prokaryote protein with homology to both conserved domains in Poldip2. These results suggest Poldip2 first appeared in Metazoans by fusion of two ancestral genes still found in bacteria, and separately coding for its conserved domains. Poldip2 is now present as a single gene in organisms as varied as sponges, sea anemones, molluscs, flat and round worms, arthropods and vertebrates. B. Ten Metazoan Poldip2 sequences were selected from BLAST results to represent a large variety of taxonomic groups. These proteins have a high percentage of identity to human Poldip2 in pairwise alignments, as shown on the right side of the panel. The left side shows a portion of a multiple sequence alignment including the last 50 residues of the DUF525 domain. Amino-acid conservation is indicated by color, from blue (10-19%) to red (100%). The rest of DUF525 and the YccV-like domain is also highly conserved across taxa (not shown). NCBI accession numbers for Homo sapiens: NP_056399.1; Gallus gallus: NP_001304285.1; Xenopus__tropicalis: NP_001017098.1; Danio__rerio: NP_997879.1; Branchiostoma__floridae: XP_002612268.1; Daphnia pulex: EFX67304.1; Bombyx_mori: XP_004926888.1; Aplysia_californica: XP_005102673.1; Hydra vulgaris: XP_002163974.2; Ciona_intestinalis: XP_002121208.2. C. Tertiary structure of the human Poldip2 DUF525 domain was predicted with similar results using two software packages: I-TASSER41-44 and Phyre2,45 based on homology to five solved ApaG structures available from the protein data bank. Homology to ApaG was sufficient to predict structure with high probability (estimated RMSD = 1.8±1.5Å in I-TASSER and 100% confidence in Phyre2). DUF525 is predicted to form a compact immunoglobulin-like beta-sandwich fold, which is represented using UCSF Chimera software,46 as ribbons colored blue to red from N to C-terminus (left) and as a space filling model with hydrophobicity increasing from blue to red (right). Hydrophobic residues at the surface of this domain could be involved in interactions with binding partners, or with other portions of Poldip2. One protein with homology to the human Poldip2YccV-like domain and of known structure is present in the protein data bank. However, relatively low homology does not allow structure prediction with high confidence (not shown).
