Figure 2. Poldip2 signal transduction pathways.
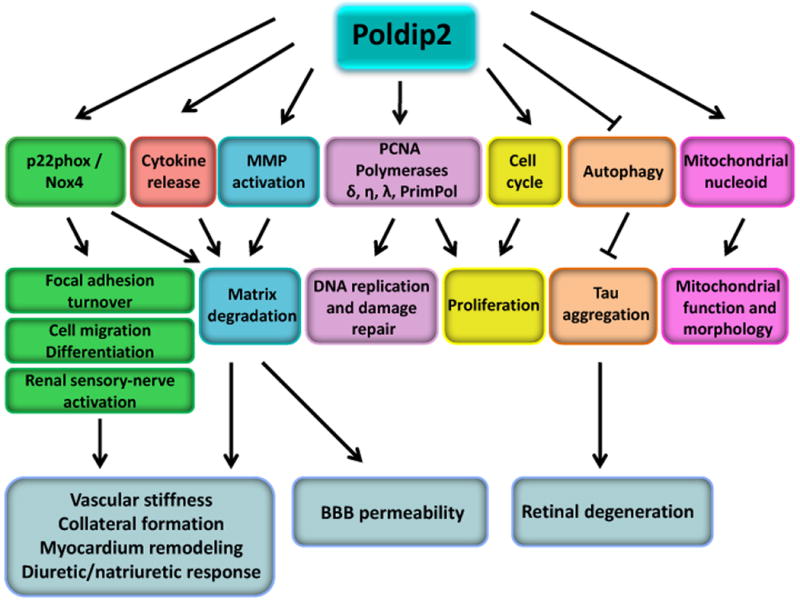
Poldip2 by itself or via interaction with its binding partners is involved in multiple signaling pathways, modulating focal adhesion turnover, ECM regulation, cell migration, proliferation and differentiation, renal sensory-nerve activation, DNA replication and damage repair, mitochondrial function and morphology and autophagy. Those processes contribute to vascular stiffness, collateral formation, myocardium remodeling, the diuretic/natriuretic response, BBB permeability and retinal degeneration. BBB, blood-brain-barrier; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; MMPs, matrix metalloproteinases.
