Figure 1. Experimental strategy to measure HIV-1 and HIV-2 mutation frequencies and spectra by single-strand consensus sequencing.
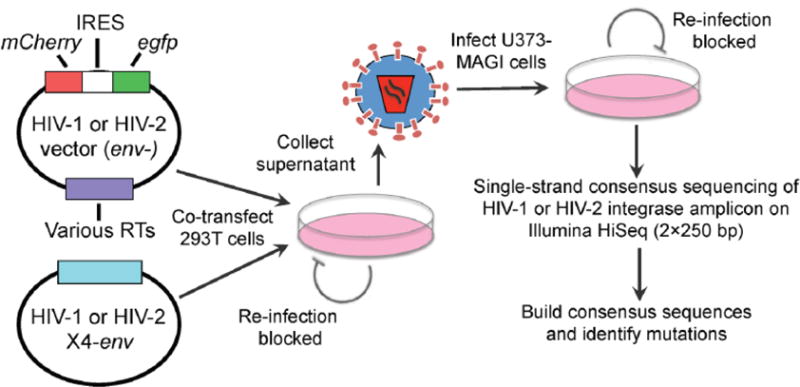
Viral stocks were produced by co-transfecting 293T cells with Env-deficient HIV-1 or HIV-2 vectors containing various HIV-1 or HIV-2 RT genes (Table 1), respectively, and HIV-1 or HIV-2 CXCR4-tropic Env expression constructs. Virus stocks were concentrated, DNase I-treated to minimize plasmid carryover, and titered in U373-MAGI-CXCR4 cells. Next, 100,000 U373-MAGI cells/sample were infected at an MOI of 1.0, and genomic DNA was purified from cells collected 72 h post-infection. Producer cells and target cells cannot be re-infected due to a lack of receptor or Env expression, respectively, such that viruses were only able to perform a single cycle of replication in this assay. Using the genomic DNAs, single-strand consensus sequencing (SSCS) was performed of homologous HIV-1 and HIV-2 integrase amplicons by uniquely tagging, exponentially amplifying, and redundantly sequencing starting templates on the Illumina HiSeq 2500, as described in Methods and Figure S1. The resulting data were used to build consensus families and determine consensus sequences, allowing identification and exclusion of PCR and sequencing errors.
