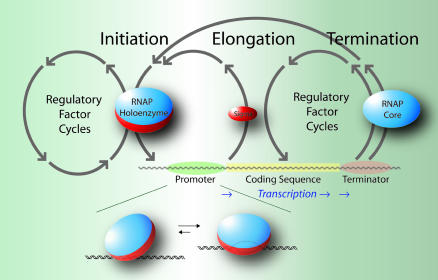
Fig. 1.
A schematic outline of the transcription cycle phases at the operon level of genomic organization. RNAP holoenzyme binds to the promoter and initiates RNA synthesis. The σ-subunit is released at the onset of elongation. RNA synthesis continues without dissociation of the RNAP core until the terminator sequence is reached when the RNA transcript and polymerase are released. The expanded diagram beneath the schematic depicts RNAP holoenzyme binding to a promoter and its isomerization to an open complex.