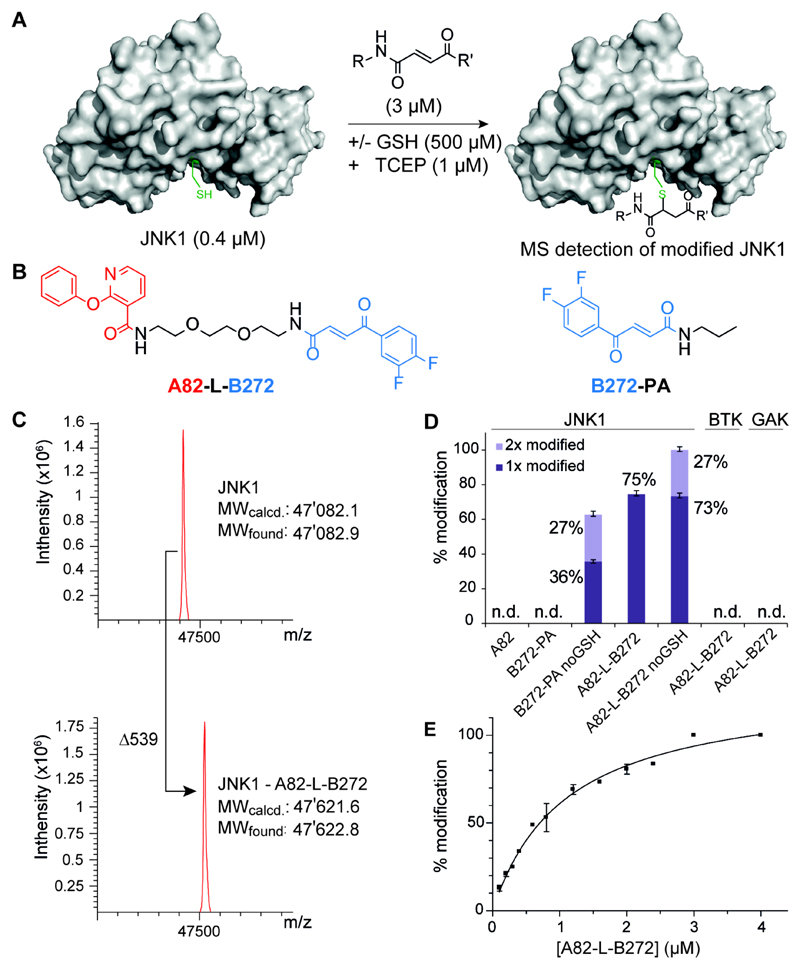
Figure 3. Mass analysis assay for covalent JNK1 binder.
(A) Schematic overview of the MS analysis assay for the detection of covalently modified JNK1 protein in the presence or absence of glutathion. (B) The most enriched fragment pair A82 and B272 connected with a short polyethyleneglycol-linker A82-L-B272 and the compound B-272 modified with a simple propylamine used as a monovalent control compound B272-PA. (C) A82-L-B272 treated JNK1 kinase domain. Mass spectra were obtained after deconvolution and show addition of 539 Daltons after incubation with A82-L-B282. Assay conditions: 0.4 µM JNK1 in 50 mM HEPES, 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 µM TCEP; 0.5 mM glutathion; 3.0 µM A82-L-B282. (D) Hit validation of selected building block pair against JNK1, BTK and GAK. By MS analysis, monovalent A82 and B272-PA show no detectable (n.d.) JNK1 modification. Assay conditions: 0.4 µM JNK1/GAK in 50 mM HEPES, 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 µM TCEP; 0.4 µM BTK in 20 mM Tris, 240 mM NaCl, 30 µM DTT; +/− glutathion (GSH, 0.5 mM); 1.6 µM binder. Error bars indicate standard deviations of three independent measurements. (E) Titration of JNK1 with increasing concentration of binder A82-L-B272. Titration conditions: 0.4 µM JNK1 in 50 mM HEPES, 300 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 µM TCEP; glutathion (GSH, 0.5 mM); 0.1 - 4.0 µM binder A82-L-B272. Error bars indicate deviations of two independent measurements.