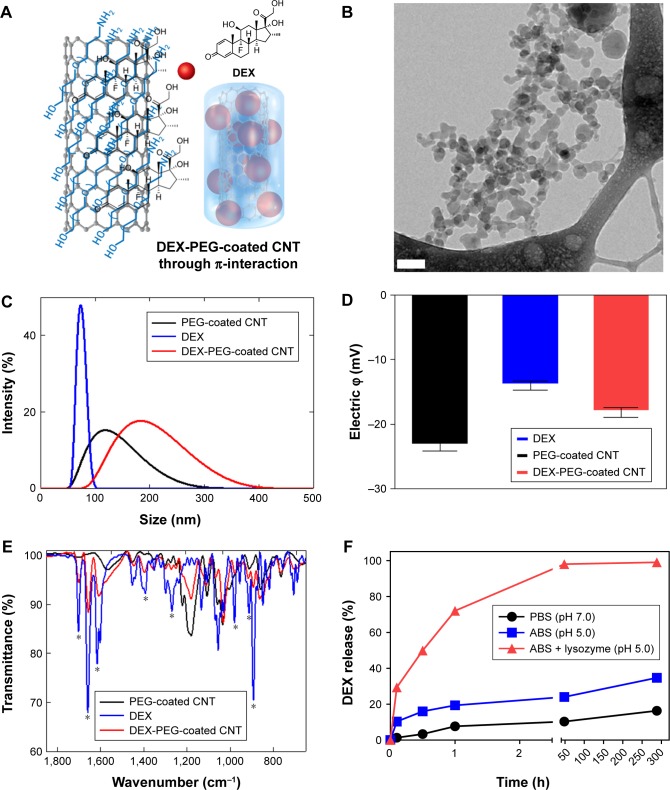
Figure 1.
Physiochemical properties and release of nanodrug.
Notes: (A) Schematic illustration of non-covalent PEG-coated DEX-CNT. (B) Cryo-TEM images show cylindrical morphologies of DEX-PEG-coated CNT. Note that PEG-coated drugs (ie, DEX) are embedded into the PEG coating. Scale bar: 100 nm. (C) Particle sizes of conventional DEX, PEG-coated CNT, and DEX-PEG-coated CNT in PBS (pH 7.0). There was a similar size distribution between DEX-PEG-coated CNT and DEX. (D) Electric potential showed that DEX-PEG-coated CNT exhibited an average charge compared to conventional DEX and PEG-coated CNT. (E) FTIR spectra of DEX-PEG-coated CNT confirmed major molecular vibration peaks from DEX and PEG-coated CNT. FTIR spectra confirm a coincidence of several IR peaks (*) between the free DEX and conjugated drugs. (F) In vitro DEX release from PEG-coated CNT was analyzed in neutral conditions (pH 7.0), acidic conditions (pH 5.0), and lysozyme-added acidic conditions (pH 5.0) for up to 288 h (both pH 7.0 and 5.0). All data represent mean ± SEM (n=3).
Abbreviations: ABS, acetate-buffered saline; CNT, carbon nanotube; Cryo-TEM, Cryo-transmission electron microscopy; DEX, dexamethasone; FTIR, Fourier transform infrared; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; PEG, polyethylene-glycol; SEM, standard error of the mean.