Figure 2.
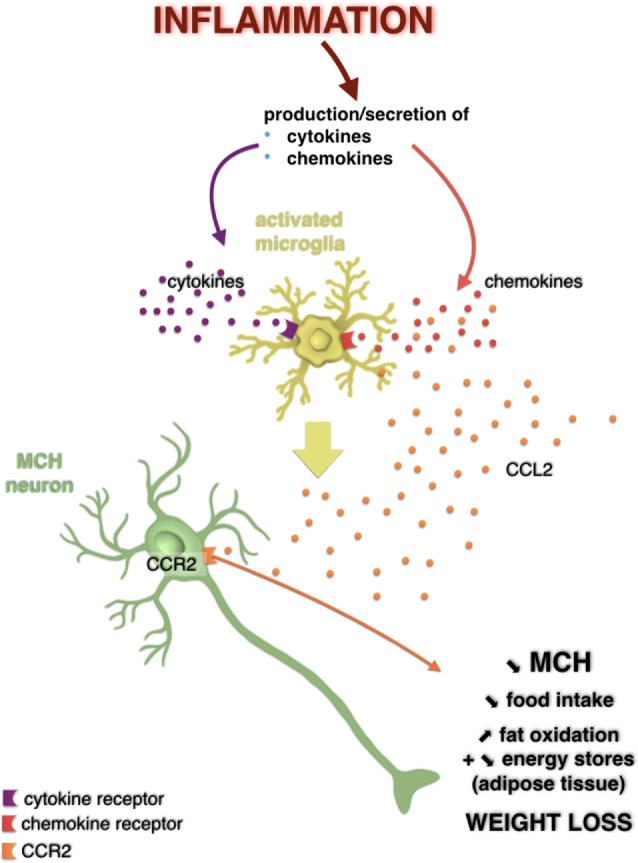
Potential action of the CC-motif chemokine ligand (CCL) 2/CCR2 signaling pathway on melanin-concentrating hormone (MCH) neurons in a weight loss model induced by a central injection of lipopolysaccharide. Hypothalamic inflammation is characterized by overexpression of inflammatory mediators such as cytokines and chemokines. It is possible that these bind to their receptors expressed by glial cells such as microglia, which then activated, can produce even more cytokines and chemokines, including CCL2. However, it is not excluded that CCL2 could act directly on MCH neurons that expressed its receptor in the lateral hypothalamus. This would result in a decreased MCH neuronal activity and in a decreased secretion of this neuropeptide, which is associated to a loss of appetite, an increased fat oxidation, likely reflecting a decrease in energy stores in adipose tissue, and thus a loss of weight. Adapted from Le Thuc and Rovère (7).
