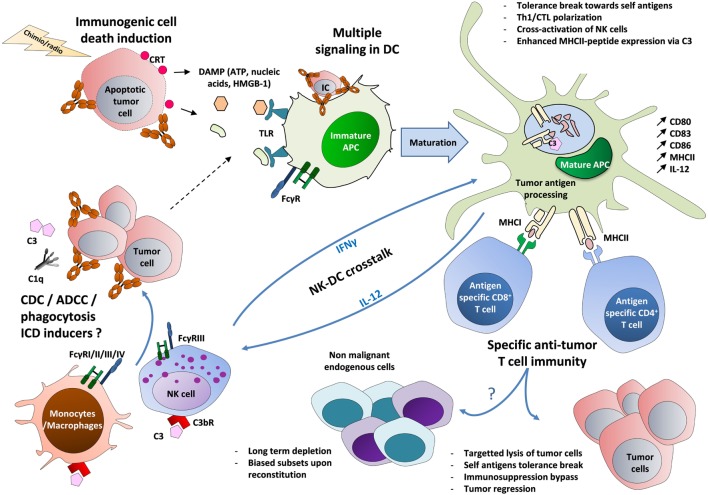
Figure 1.
The circuits of the vaccinal effect of monoclonal antibodies in cancer. Tumor cells opsonized with antibodies recruit C1q molecule and FcγR-expressing innate cells, such as macrophages and NK cells (63–84). This leads to cell lysis and to the formation of cell debris through phagocytosis, ADCC, and CDC (5, 6). Immature DCs then capture the resulting immune complexes (made of Ag-containing tumor lysate and antibody) (57–61). In parallel, tumor cells treated by radiotherapy or chemotherapy may undergo ICD, leading to the exposure of CRT on the surface of dying cells and to the release of ATP and HMGB-1. The latter molecule triggers TLR-mediated inflammation (22–24). These multiple signals then lead to DC maturation (upregulation of MHC II, CD80, CD83, and CD86) and to the production of Th1-prone cytokines (IFNγ, IL-12) (85, 86). A tolerance break can occur, marked by the presentation of tumor-associated self-antigens on MHC I and MHC II, possibly reinforced by the capacity of C3 to enhance MHC II exposure (57–61, 87). The activation of IL-12-producing DCs could also be strengthened by a positive cross-talk with IFNγ-producing NK cells, leading to a stronger activation of both cell types (64, 65). Altogether, these mechanisms lead to the priming of self-reactive tumor-specific CD4+ and CD8+ T cells that can act back against tumor cells and eventually circumvent the pro-tumor immunosuppression (regulatory T cells, IL-10, TGF-β, etc.) (Table 1). These self-reactive T cells could also impact endogenous cells expressing the same targeted antigens, with a long-term depletion and biased subsets upon reconstitution (25–33). FcγRIV is only expressed in mouse on myeloid cells. ADCC, antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity; APC, antigen-presenting cell; CDC, complement-dependent cytotoxicity; CRT, calreticulin; CTL, cytotoxic T lymphocyte; C3bR, receptor for the C3b complement fragment; DCs, dendritic cells; IC, immune complex; ICD, immunogenic cell death; DAMP, damage-associated molecular pattern; FcγR, receptors for the Fc region of IgG; HMGB-1, high-mobility group box 1 protein; MHC, major histocompatibility complex; TLR, toll-like receptor.