Fig. 7.
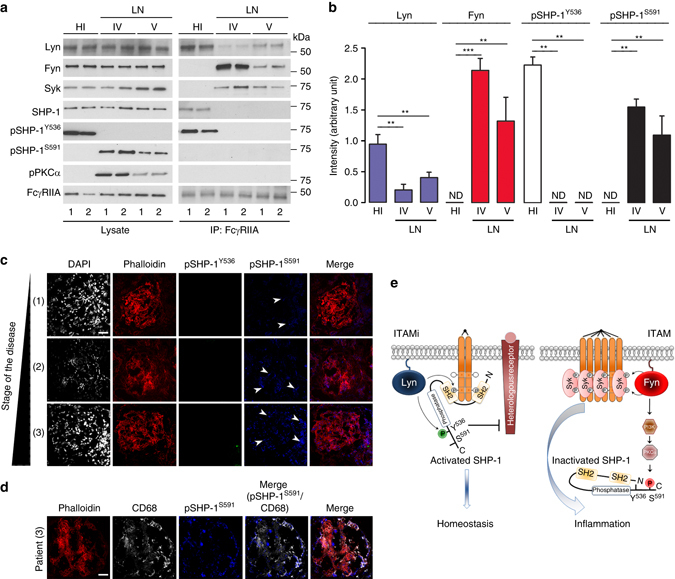
Fyn-SHP-1S591 axis as a biomarker of lupus nephritis activity. a Analysis of phosphorylated ITAM effectors in blood leukocyte samples from 4 lupus nephritis (LN) patients (1 and 2 are class IV; 3 and 4 are class V) and four healthy individuals (HI). Left panel, cell lysates were immunoblotted using indicated Abs. Right panel, FcγRIIA immunoprecipitation (IP) with an anti-FcγRIIA monoclonal antibody (IV.3) followed by immunoblotting using indicated antibodies. b Quantification of the indicated band using ImageJ software relative to total levels of the corresponding protein in cell lysates. *P < .05, **P < .01, ***P < .001; Mann–Whitney test. Not detectable (ND). Data are mean ± s.e.m (n = 5). No significant differences in blood phagocyte counts were observed between healthy controls and patients as followed: Monocytes 0.50 ± 0.16 vs. 0.49 ± 0.30; Neutrophils 4.0 ± 0.42 vs. 3.4 ± 2.4, ×106/ml, respectively. c Representative photomicrographs of glomeruli stained from biopsies of lupus nephritis patients for phalloidin (red), p-SHP-1S591-Alexa 647 (blue), and pSHP-1Y536-Alexa 488 (green). Scale bars: 200 μm. d Representative photomicrographs of glomeruli stained from biopsies of LN patients for phalloidin (red), p-SHP-1S591-Alexa 647 (blue), and CD68-Alexa 405 (white). Scale bars: 200 μm. e Predicted model for the Lyn and Fyn switch controlling the balance between inhibitory or activating ITAM signals in immunoreceptors. Left panel: upon divalent targeting of immunoreceptors, Lyn is recruited to the receptor leading to receptor partial phosphorylation on tyrosine (e.g., Y304 in the case of FcγRIIA11). Simultaneously, Lyn phosphorylates SHP-1 on Y536, inducing a conformational change leading to SH2 domain recruitment to phospho-ITAM, thereby lifting inhibition of the phosphatase domain by the N-SH2 domain. This enables SHP-1 to inactivate signal effectors recruited by heterologous receptors. Right panel: multivalent crosslinking of immunoreceptors results in full phosphorylation of ITAM tyrosines by Fyn. These phosphotyrosines serve as “docking” sites for Syk, inducing cell activation and inflammatory responses. Fyn simultaneously activates the PI3K–PKCα pathway, leading to SHP-1 phosphorylation on S591. The N-SH2/phosphatase domains are maintained in a closed conformation, blocking both recruitment and activation of SHP-1. Under chronic stimulation, this may lead to aggravation of inflammatory or autoimmune diseases
