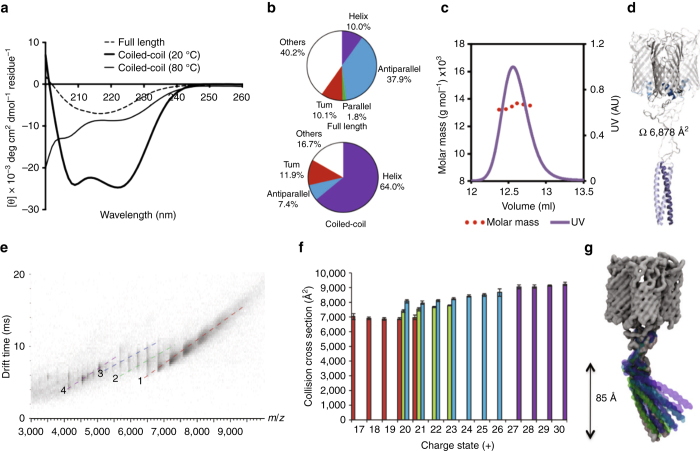
Fig. 3.
Biophysical characterisation of the FapF N-terminal coiled coil. a Far-UVCD spectra for the full-length FapF (dashed line) and the coiled-coil peptide (D3–Q40) at 20 °C (thick solid line) and 80 °C (thin solid line). b Secondary structure composition for full-length FapF and the coiled-coil peptide (20 °C) as estimated by the BeStSel method. c SEC-MALS profile of the coiled-coil indicating a monodisperse sample corresponding to the trimer. d Atomistic model of full-length FapF coloured corresponding to the structural boundaries shown in Fig. 1a. The theoretical CCS of this model is shown. e Ion-mobility measurements for purified full-length FapF. These indicate a population of four main substate populations. f Collision cross-sections of the four different FapF trimer populations. Error bars are derived from an average of three different wave heights. g Motion of the N-terminal domain of full-length FapF observed during coarse-grained simulations. The trajectory was aligned to the barrel and the position of the N-terminal domain at 10 ns intervals are shown (grey=0 ns, green=10 ns, blue=20 ns, purple=30 ns)