Figure 2.
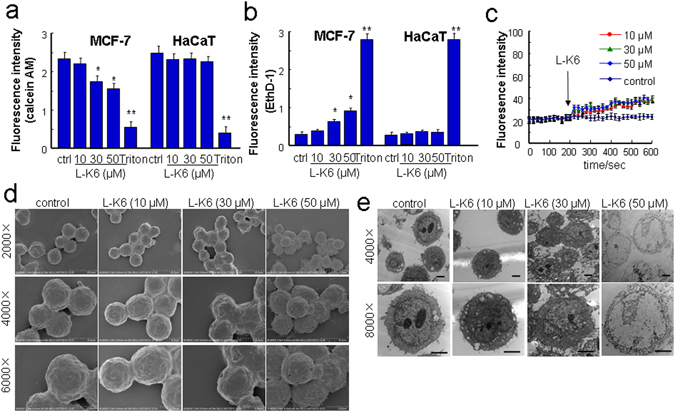
L-K6 at higher concentrations preferentially elevated cancer cell membrane permeability. To evaluate the possible impacts of L-K6 on cell membrane permeability, a calcein/EthD-1 leakage assay was performed. L-K6 administration (especially 30~50 μM) induced a significant change in membrane permeability of MCF-7 cells, as indicated by the decreased fluorescence intensities of calcein (a) and increased EthD-1 (b). Additionally, L-K6-induced elevation of membrane permeability was cancer-specific, as evidenced by stable fluorescence intensities of calcein and EthD-1 in HaCaT cells (a,b). Consistent with calcein/EthD-1 leakage assay, the membrane depolarization assay further supported the elevated membrane permeability (mean ± SD) as indicated by the increased DiBAC4(3) fluorescence intensity after peptides exposure (c). Morphological changes of human MCF-7 breast cancer cells induced by L-K6 as assessed by scanning electron microscopy (d) and transmission electron microscopy (e). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 vs. untreated control group. All experiments had been performed in triplicate.
