Figure 6.
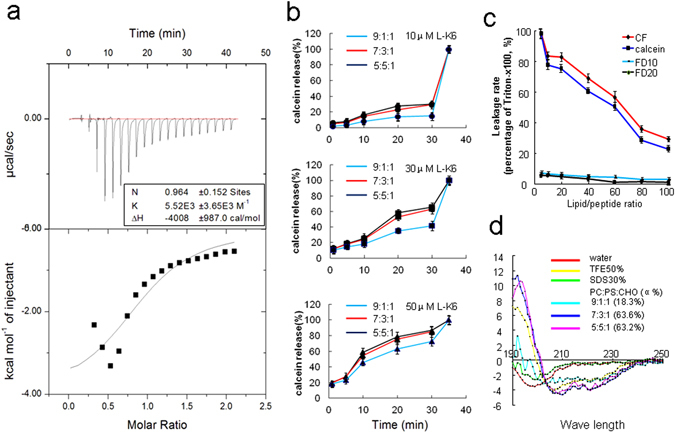
L-K6 elevated the liposome permeability through a PS-related mechanism. The ITC data suggested the direct binding of the positively charged L-K6 to the negatively charged PS (a). Consistent with the data from the cell-based system, co-incubation of L-K6 with the liposomes caused rapid leakage of calcein from the liposomes in a dose-dependent manner. In addition, this leakage activity was PS-associated, as shown by an elevated calcein intensity with increased PS content of liposome (from 9:1:1 to 7:3:1 or 5:5:1) (b). Interestingly, calcein and carboxyfluorescein (CF) were released from the liposome, whereas FD10 and FD20, two fluorescent dyes with a molecular weight over 10kD, were resistant to be released (c). Moreover, the higher ratio of PS content in liposome yielded a higher percentage of α-helical structure, as assessed by circular dichroism spectroscopy (d). All experiments had been performed in triplicate. All data were expressed as mean ± SD.
