Figure 4.
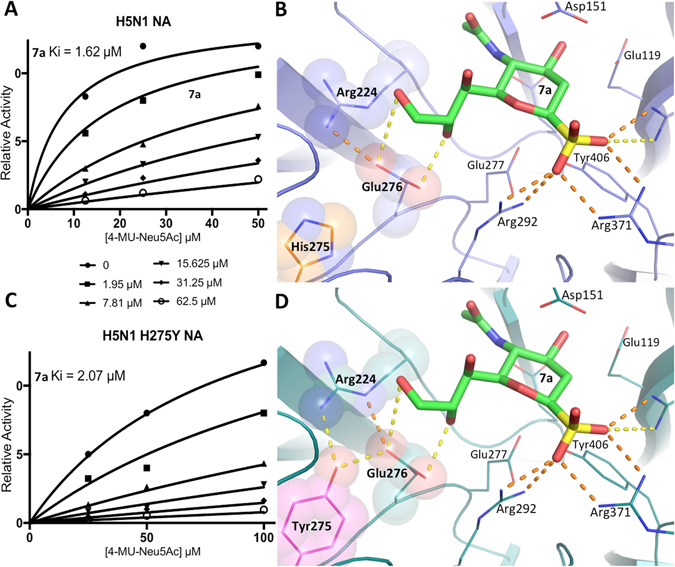
Inhibition of avian-origin H5N1 N1 by sulfo-sialic acid analogue 7a. (A) 7a inhibits wildtype N1 with an inhibitory constant (K i) of 1.62 μM. (B) Predicted binding of 7a to the wildtype N1 active site. (C) 7a inhibits His275Tyr oseltamivir-resistant N1 with a similar potency to that of wildtype N1. (D) Predicted binding of 7a to the His275Tyr N1 active site shows that the 7a glycerol side chain maintains the same interactions with the Glu276 side chain. Key residues relating to His275Tyr drug resistance are shown inside transparent spheres. Electrostatic interactions of the inhibitor sulfo group and glycerol moiety are indicated by dashed lines, with stronger ionic interactions colored orange. The binding analysis was performed with MOE based on the structure of A/Vietnam/1203/04 (H5N1) NA (PDB ID 3CKZ)26.
