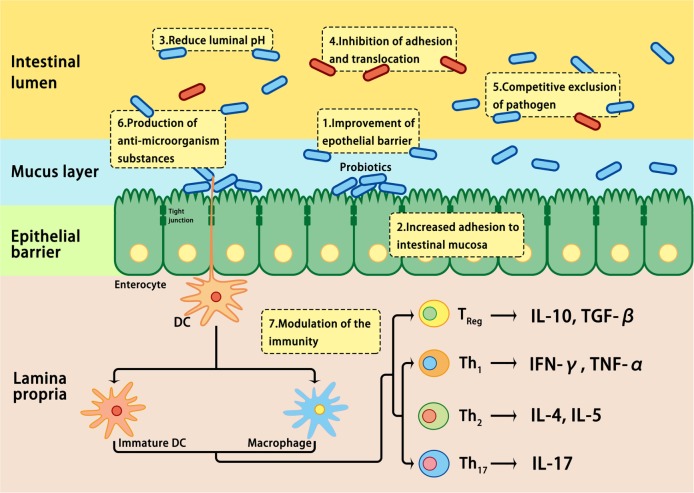
Figure 3.
Mechanisms involved in probiotic-induced protection against intestinal dysbiosis. Probiotics suppress pathogens through various actions, including lowering luminal pH, production of antimicrobial proteins, inhibition of adhesion and translocation of flora, competitive exclusion of pathogens, improvement of epithelial barrier, enhancement of adhesion of commensal bacteria to the intestinal mucosa, and modulation of gastrointestinal mucosal immune system.