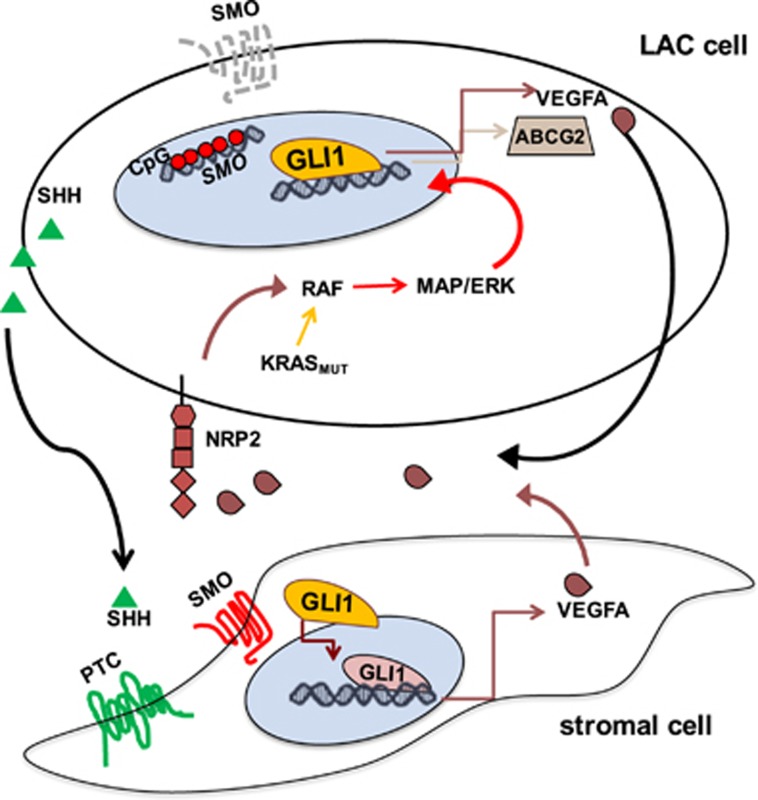
Figure 7.
Noncanonical GLI1 signaling sustaining LAC growth and CSC maintenance. The HH pathway effector GLI1 can be activated even in the absence of SMO, the canonical upstream activator of HH signaling, whose expression is epigenetically silenced in many GLI1-expressing LACs. GLI1 serves as a downstream effector of oncogenic MAPK/ERK signaling, which can be triggered by ligand-binding events at NRP2 receptors expressed by the cancer cells. GLI1 then promotes features involved in tumor growth and CSC maintenance, including the transcription of known HH target genes (for example, ABCG2 and VEGFA). The VEGFA that binds epithelial-cell NRP2 receptors is secreted by the epithelial cells themselves, and this autocrine signaling loop is self-amplified by GLI1-upregulated transcription of both the receptor (NRP2) and its ligand (VEGFA). NRP2/ERK/GLI signaling can also be activated in a paracrine fashion by VEGFA secreted by cells in the tumor stroma. The stromal VEGFA production is the result of canonical SMO-dependent HH–GLI signaling triggered by SHH secreted by epithelial cells. The output of this stromal signaling includes VEGFA, which in turn bind tumor-cell NRP2, thereby triggering the noncanonical MAPK/ERK-mediated GLI1 activation illustrated in the upper panel.