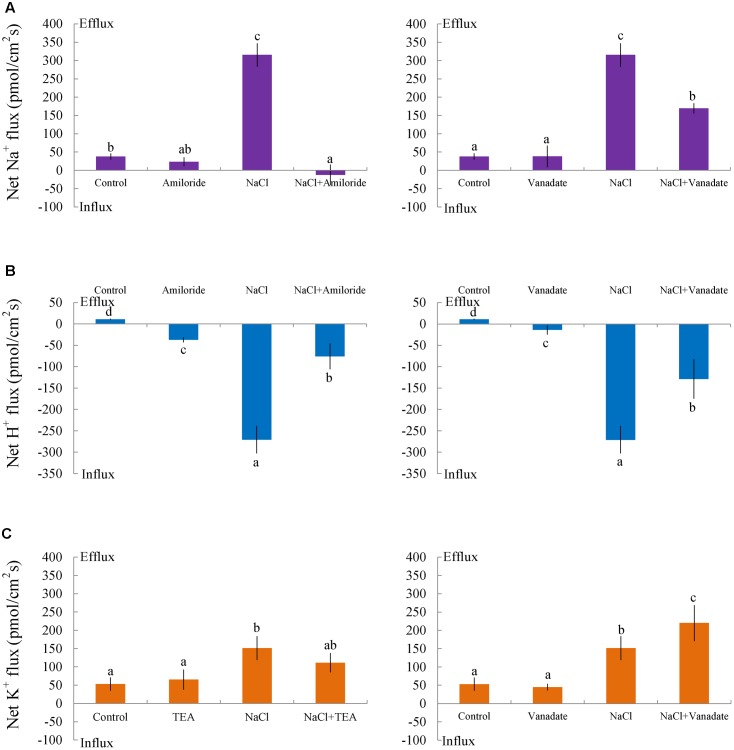
FIGURE 5.
Effects of amiloride, sodium orthovanadate, and tetraethylammonium (TEA) on Na+, K+, and H+ fluxes in G. uralensis roots under salt stress. Roots were exposed to 0 (control) or 100 mM NaCl (NaCl) for 24 h, then exposed to transporter/channel inhibitors for 30 min. Steady-state fluxes were measured along the root axis at the apical zones (200–2700 μm from the root tip). Mean fluxes of (A) Na+ and (B) H+ were measured in the absence and presence of inhibitors, (left) amiloride (50 μM) and (right) sodium orthovanadate (500 μM). (C) The mean K+ flux was measured in the absence and presence of inhibitors, (left) TEA (50 μM) and (right) sodium orthovanadate (500 μM). Bars (±SD) represent the means of five to six individual plants; letters (a, b, c, and d) indicate significant differences between treatments (P < 0.05).